Sirtuin/Sir2 phylogeny, evolutionary considerations and structural conservation
- PMID: 19936627
- PMCID: PMC3710699
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-009-0169-x
Sirtuin/Sir2 phylogeny, evolutionary considerations and structural conservation
Abstract
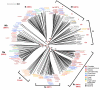
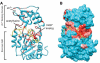
The sirtuins are a protein family named after the first identified member, S. cerevisiae Sir2p. Sirtuins are protein deacetylases whose activity is dependent on NAD(+) as a cosubstrate. They are structurally defined by two central domains that together form a highly conserved catalytic center, which catalyzes the transfer of an acetyl moiety from acetyllysine to NAD(+), yielding nicotinamide, the unique metabolite O-acetyl-ADP-ribose and deacetylated lysine. One or more sirtuins are present in virtually all species from bacteria to mammals. Here we describe a phylogenetic analysis of sirtuins. Based on their phylogenetic relationship, sirtuins can be grouped into over a dozen classes and subclasses. Humans, like most vertebrates, have seven sirtuins: SIRT1-SIRT7. These function in diverse cellular pathways, regulating transcriptional repression, aging, metabolism, DNA damage responses and apoptosis. We show that these seven sirtuins arose early during animal evolution. Conserved residues cluster around the catalytic center of known sirtuin family members.
Figures
References
-
- Ahuja N, Schwer B, Carobbio S, Waltregny D, North BJ, Castronovo V, Maechler P, Verdin E. Regulation of insulin secretion by SIRT4, a mitochondrial ADP-ribosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:33583–33592. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio OM, Billington BL, Gottschling DE. Modifiers of position effect are shared between telomeric and silent mating-type loci in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991;66:1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Avalos JL, Celic I, Muhammad S, Cosgrove MS, Boeke JD, Wolberger C. Structure of a Sir2 enzyme bound to an acetylated p53 peptide. Mol. Cell. 2002;10:523–535. - PubMed
-
- Baldauf SL. The deep roots of eukaryotes. Science. 2003;300:1703–1706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

