Computer-aided detection of intracranial aneurysms in MR angiography
- PMID: 19937083
- PMCID: PMC3046787
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-009-9254-0
Computer-aided detection of intracranial aneurysms in MR angiography
Abstract
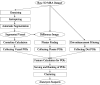
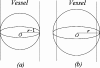
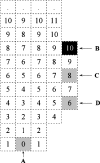
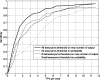
Intracranial aneurysms represent a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. While the risk factors for aneurysm formation are known, the detection of aneurysms remains challenging. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) has recently emerged as a useful non-invasive method for aneurysm detection. However, even for experienced neuroradiologists, the sensitivity to small (<5 mm) aneurysms in MRA images is poor, on the order of 30~60% in recent, large series. We describe a fully automated computer-aided detection (CAD) scheme for detecting aneurysms on 3D time-of-flight (TOF) MRA images. The scheme locates points of interest (POIs) on individual MRA datasets by combining two complementary techniques. The first technique segments the intracranial arteries automatically and finds POIs from the segmented vessels. The second technique identifies POIs directly from the raw, unsegmented image dataset. This latter technique is useful in cases of incomplete segmentation. Following a series of feature calculations, a small fraction of POIs are retained as candidate aneurysms from the collected POIs according to predetermined rules. The CAD scheme was evaluated on 287 datasets containing 147 aneurysms that were verified with digital subtraction angiography, the accepted standard of reference for aneurysm detection. For two different operating points, the CAD scheme achieved a sensitivity of 80% (71% for aneurysms less than 5 mm) with three mean false positives per case, and 95% (91% for aneurysms less than 5 mm) with nine mean false positives per case. In conclusion, the CAD scheme showed good accuracy and may have application in improving the sensitivity of aneurysm detection on MR images.
Figures
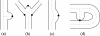






Similar articles
-
Diagnostic accuracy of 3D time-of-flight MR angiography compared with digital subtraction angiography for follow-up of coiled intracranial aneurysms: influence of aneurysm size.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Apr;28(4):628-34. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17416811 Free PMC article.
-
Automated unruptured cerebral aneurysms detection in TOF MR angiography images using dual-channel SE-3D UNet: a multi-center research.Eur Radiol. 2023 May;33(5):3532-3543. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09385-z. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36725720
-
Computerized detection of intracranial aneurysms for three-dimensional MR angiography: feature extraction of small protrusions based on a shape-based difference image technique.Med Phys. 2006 Feb;33(2):394-401. doi: 10.1118/1.2163389. Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 16532946
-
MRA versus DSA for the follow-up imaging of intracranial aneurysms treated using endovascular techniques: a meta-analysis.J Neurointerv Surg. 2019 Oct;11(10):1009-1014. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-014936. Epub 2019 May 2. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019. PMID: 31048457 Review.
-
Intracranial aneurysm detection: an object detection perspective.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Sep;19(9):1667-1675. doi: 10.1007/s11548-024-03132-z. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 38632166 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of intracranial aneurysms using deep learning-based CAD system: usefulness of the scores of CNN's final layer for distinguishing between aneurysm and infundibular dilatation.Jpn J Radiol. 2023 Feb;41(2):131-141. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01341-7. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Jpn J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36173510 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Automated Brain Aneurysm Detection in TOF-MRA: Open Data, Weak Labels, and Anatomical Knowledge.Neuroinformatics. 2023 Jan;21(1):21-34. doi: 10.1007/s12021-022-09597-0. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Neuroinformatics. 2023. PMID: 35982364 Free PMC article.
-
Convolutional Neural Networks for the Detection and Measurement of Cerebral Aneurysms on Magnetic Resonance Angiography.J Digit Imaging. 2019 Oct;32(5):808-815. doi: 10.1007/s10278-018-0162-z. J Digit Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30511281 Free PMC article.
-
Fast inversion recovery magnetic resonance angiography of the intracranial arteries.Magn Reson Med. 2010 Jun;63(6):1648-58. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22456. Magn Reson Med. 2010. PMID: 20512868 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Artificial Intelligence in Cerebrovascular Disease Imaging: Applications and Challenges.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(7):1359-1382. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666211108141446. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34749621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Korogi Y, Takahashi M, Mabuchi N, Nakagawa T, Fujiwara S, Horikawa Y, Miki H, O’Uchi T, Shiga H, Shiokawa Y, Watabe T, Furuse M. Intracranial aneurysms: diagnostic accuracy of MR angiography with evaluation of maximum intensity projection and source images. Radiology. 1996;199:199–207. - PubMed
-
- White PM, Teasdale EM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V. Intracranial aneurysms: CT angiography and MR angiography for detection prospective blinded comparison in a large patient cohort. Radiology. 2001;219:739–749. - PubMed
-
- Arimura H, Li Q, Korogi Y, Hirai T, Abe H, Yamashita Y, Katsuragawa S, Ikeda R, Doi K. Automated computerized scheme for detection of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in three dimensional magnetic resonance angiography. Acad Radiol. 2004;11:1093–1104. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2004.07.011. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

