Intra-brain microinjection of human mesenchymal stem cells decreases allodynia in neuropathic mice
- PMID: 19937263
- PMCID: PMC11115751
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0202-4
Intra-brain microinjection of human mesenchymal stem cells decreases allodynia in neuropathic mice
Abstract
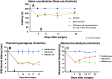
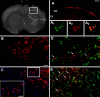
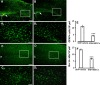
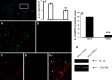
Neuropathic pain is a very complex disease, involving several molecular pathways. Current available drugs are usually not acting on the several mechanisms underlying the generation and propagation of pain. We used spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain to assess the possible use of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) as anti-neuropathic tool. Human MSCs were transplanted in the mouse lateral cerebral ventricle. Stem cells injection was performed 4 days after sciatic nerve surgery. Neuropathic mice were monitored 7, 10, 14, 17, and 21 days after surgery. hMSCs were able to reduce pain-like behaviors, such as mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia, once transplanted in cerebral ventricle. Anti-nociceptive effect was detectable from day 10 after surgery (6 days post cell injection). Human MSCs reduced the mRNA levels of the pro-inflammatory interleukin IL-1beta mouse gene, as well as the neural beta-galactosidase over-activation in prefrontal cortex of SNI mice. Transplanted hMSCs were able to reduce astrocytic and microglial cell activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-lasting effects of human mesenchymal stem cell systemic administration on pain-like behaviors, cellular, and biomolecular modifications in neuropathic mice.Front Integr Neurosci. 2011 Dec 1;5:79. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2011.00079. eCollection 2011. Front Integr Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22164136 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells in the study of neuropathic pain.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;617:337-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-323-7_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20336433
-
Systemic administration of human adipose-derived stem cells reverts nociceptive hypersensitivity in an experimental model of neuropathy.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Apr 15;22(8):1252-63. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0398. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23190263 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal Injection of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain in Rats.Neurochem Res. 2016 Dec;41(12):3250-3260. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2051-5. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27655256
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation for Neuropathic Pain Induced By Peripheral Nerve Injury in Animal Models: A Systematic Review.Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Nov 15;29(22):1420-1428. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0131. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Stem Cells Dev. 2020. PMID: 32962522
Cited by
-
The effect of human mesenchymal stem cell injection on pain behavior in chronic post-ischemia pain mice.Korean J Pain. 2020 Jan 1;33(1):23-29. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.1.23. Korean J Pain. 2020. PMID: 31888314 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Human Amniotic Fluid Derived Stem Cells in Alleviation of Neuropathic Pain in Chronic Constrictive Injury Nerve Model.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 21;11(7):e0159482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159482. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27441756 Free PMC article.
-
Autism spectrum disorders: is mesenchymal stem cell personalized therapy the future?J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:480289. doi: 10.1155/2012/480289. Epub 2012 Feb 13. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22496609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell therapy in pain medicine.Korean J Pain. 2019 Oct 1;32(4):245-255. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.4.245. Korean J Pain. 2019. PMID: 31569916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells to treat diabetic neuropathy: a long and strenuous way from bench to the clinic.Cell Death Discov. 2016 Jul 11;2:16055. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.55. eCollection 2016. Cell Death Discov. 2016. PMID: 27551543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Merskey H, Bogduk N. Classification of chronic pain. Seattle: IASP; 1994.
-
- de Novellis V, Siniscalco D, Galderisi U, Fuccio C, Nolano M, Santoro L, Cascino A, Roth KA, Rossi F, Maione S. Blockade of glutamate mGlu5 receptors in a rat model of neuropathic pain prevents early over-expression of pro-apoptotic genes and morphological changes in dorsal horn lamina II. Neuropharmacology. 2004;46:468–479. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.10.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siniscalco D, Fuccio C, de Novellis V, Rossi F, Maione S. Molecular methods for neuropathic pain treatment. J Neuropathic Pain. 2005;1(3):35–42. doi: 10.1300/J426v01n03_04. - DOI
-
- Galluzi KE. Management of neuropathic pain. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2005;105:12–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

