Influence of the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip by the abduction brace on locomotor development in children
- PMID: 19937280
- PMCID: PMC2811674
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-009-0219-0
Influence of the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip by the abduction brace on locomotor development in children
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the influence of treating developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) with the abduction brace on locomotor development in children.
Methods: One hundred children treated for DDH served as the study group. There were 80 girls and 20 boys. The children's average age at the beginning of the treatment was 8 weeks. The control group consisted of 100 healthy children with normal hips and without any locomotor system disorders. We have evaluated factors such as the age at which the treatment started, the duration of the treatment, the birth weight of the child and the time when the children started sitting and walking independently.
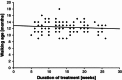
Results: On average, treatment with the abduction brace lasted 13 weeks (ranging from 6 to 26 weeks). The mean age at which the patients began to sit was 7 months, which was one week later compared to children from the control group (P = 0.28). The age at which they started walking was 12 months and 2 weeks, which was 3 weeks later than in the control group (P = 0.002).
Conclusion: For children with DDH, the abduction brace is a safe and effective method of treatment and, although the infants begin to walk about 3 weeks later compared to healthy children, this practice does not seriously affect the child's locomotor development.
Figures
References
-
- Wood MKMA, Conboy V, Benson MKD. Does early treatment by abduction splintage improve the development of dysplastic but stable neonatal hips? J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20:302–305. - PubMed
-
- Czubak J, Kruczyński J (2003) Rozwojowa dysplazja i zwichnięcie stawu biodrowego. In: Marciniak W, Szulc A (eds) Wiktora Degi ortopedia i rehabilitacja. Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL, Warszawa, p 165
-
- Koszla MM. An apparatus for the treatment of congenital hip dysplasia. Chir Narządów Ruchu Ortop Pol. 1964;29:403–405. - PubMed
-
- Fredensborg N. The results of early treatment of typical congenital dislocation of the hip in Malmö. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976;58:272–278. - PubMed
-
- Mostert AK, Tulp NJ, Castelein RM. Results of Pavlik harness treatment for neonatal hip dislocation as related to Graf’s sonographic classification. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20:306–310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials