CAS proteins in normal and pathological cell growth control
- PMID: 19937461
- PMCID: PMC2836406
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0213-1
CAS proteins in normal and pathological cell growth control
Abstract
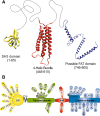
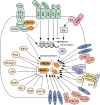
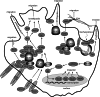
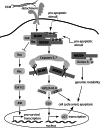
Proteins of the CAS (Crk-associated substrate) family (BCAR1/p130Cas, NEDD9/HEF1/Cas-L, EFS/SIN and CASS4/HEPL) are integral players in normal and pathological cell biology. CAS proteins act as scaffolds to regulate protein complexes controlling migration and chemotaxis, apoptosis, cell cycle, and differentiation, and have more recently been linked to a role in progenitor cell function. Reflecting these complex functions, over-expression of CAS proteins has now been strongly linked to poor prognosis and increased metastasis in cancer, as well as resistance to first-line chemotherapeutics in multiple tumor types including breast and lung cancers, glioblastoma, and melanoma. Further, CAS proteins have also been linked to additional pathological conditions including inflammatory disorders, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, as well as developmental defects. This review will explore the roles of the CAS proteins in normal and pathological states in the context of the many mechanistic insights into CAS protein function that have emerged in the past decade.
Figures
References
-
- Brinkman A, van der Flier S, Kok EM, Dorssers LC. BCAR1, a human homologue of the adapter protein p130Cas, and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:112–120. - PubMed
-
- Ishino M, Ohba T, Sasaki H, Sasaki T. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a phosphoprotein, Efs, which contains a Src homology 3 domain and associates with Fyn. Oncogene. 1995;11:2331–2338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

