Potentially amyloidogenic conformational intermediates populate the unfolding landscape of transthyretin: insights from molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 19937650
- PMCID: PMC2865717
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.289
Potentially amyloidogenic conformational intermediates populate the unfolding landscape of transthyretin: insights from molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
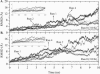
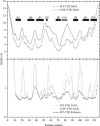
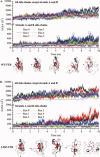
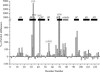
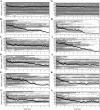
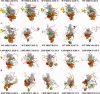
Protein aggregation into insoluble fibrillar structures known as amyloid characterizes several neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, Huntington's and Creutzfeldt-Jakob. Transthyretin (TTR), a homotetrameric plasma protein, is known to be the causative agent of amyloid pathologies such as FAP (familial amyloid polyneuropathy), FAC (familial amyloid cardiomiopathy) and SSA (senile systemic amyloidosis). It is generally accepted that TTR tetramer dissociation and monomer partial unfolding precedes amyloid fibril formation. To explore the TTR unfolding landscape and to identify potential intermediate conformations with high tendency for amyloid formation, we have performed molecular dynamics unfolding simulations of WT-TTR and L55P-TTR, a highly amyloidogenic TTR variant. Our simulations in explicit water allow the identification of events that clearly discriminate the unfolding behavior of WT and L55P-TTR. Analysis of the simulation trajectories show that (i) the L55P monomers unfold earlier and to a larger extent than the WT; (ii) the single alpha-helix in the TTR monomer completely unfolds in most of the L55P simulations while remain folded in WT simulations; (iii) L55P forms, early in the simulations, aggregation-prone conformations characterized by full displacement of strands C and D from the main beta-sandwich core of the monomer; (iv) L55P shows, late in the simulations, severe loss of the H-bond network and consequent destabilization of the CBEF beta-sheet of the beta-sandwich; (v) WT forms aggregation-compatible conformations only late in the simulations and upon extensive unfolding of the monomer. These results clearly show that, in comparison with WT, L55P-TTR does present a much higher probability of forming transient conformations compatible with aggregation and amyloid formation.
Figures
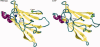

References
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM. Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:333–366. - PubMed
-
- Brito RMM, Damas AM, Saraiva MJ. Amyloid formation by transthyretfrom protein stability to protein aggregation. Curr Med Chem Immunol Endocr Metab Agents. 2003;3:349–360.
-
- Andrade C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy. Familial atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952;75:408–427. - PubMed
-
- Connors LH, Richardson AM, Theberge R, Costello CE. Tabulation of transthyretin (TTR) variants as of 1/1/2000. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;7:54–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

