VCD spectroscopic properties of the beta-hairpin forming miniprotein CLN025 in various solvents
- PMID: 19937759
- PMCID: PMC4499852
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.21356
VCD spectroscopic properties of the beta-hairpin forming miniprotein CLN025 in various solvents
Abstract
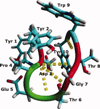
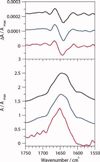
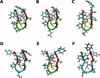
Electronic and vibrational circular dichroism are often used to determine the secondary structure of proteins, because each secondary structure has a unique spectrum. Little is known about the vibrational circular dichroic spectroscopic features of the beta-hairpin. In this study, the VCD spectral features of a decapeptide, YYDPETGTWY (CLN025), which forms a stable beta-hairpin that is stabilized by intramolecular weakly polar interactions and hydrogen bonds were determined. Molecular dynamics simulations and ECD spectropolarimetry were used to confirm that CLN025 adopts a beta-hairpin in water, TFE, MeOH, and DMSO and to examine differences in the secondary structure, hydrogen bonds, and weakly polar interactions. CLN025 was synthesized by microwave-assisted solid phase peptide synthesis with N(alpha)-Fmoc protected amino acids. The VCD spectra displayed a (-,+,-) pattern with bands at 1640 to 1656 cm(-1), 1667 to 1687 cm(-1), and 1679 to 1686 cm(-1) formed by the overlap of a lower frequency negative couplet and a higher frequency positive couplet. A maximum IR absorbance was observed at 1647 to 1663 cm(-1) with component bands at 1630 cm(-1), 1646 cm(-1), 1658 cm(-1), and 1675 to 1680 cm(-1) that are indicative of the beta-sheet, random meander, either random meander or loop and turn, respectively. These results are similar to the results of others, who examined the VCD spectra of beta-hairpins formed by (D)Pro-Xxx turns and indicated that observed pattern is typical of beta-hairpins.
Figures




References
-
- Ptitsyn OB. FEBS Lett. 1991;131:197. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez-Alvarado M, Kortemme T, Blanco FJ, Serrano L. Bioorg & Med Chem. 1999;7:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Maynard AJ, Sharman GJ, Searle MS. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:1996–2007.
-
- Andersen NH, Dyer RB, Fesinmeyer RM, Gai F, Liu Z, Neidigh JW, Tong H. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:9879–9880.
-
- Palermo NY, Csontos J, Owen MC, Murphy RF, Lovas S. J Comput Chem. 2007;28:1208–1214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

