Calpain activation and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger degradation occur downstream of calcium deregulation in hippocampal neurons exposed to excitotoxic glutamate
- PMID: 19937813
- PMCID: PMC2830319
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.22295
Calpain activation and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger degradation occur downstream of calcium deregulation in hippocampal neurons exposed to excitotoxic glutamate
Abstract
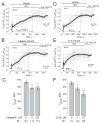
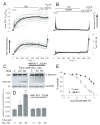
Delayed calcium deregulation (DCD) plays an essential role in glutamate excitotoxicity, a major detrimental factor in stroke, traumatic brain injury, and various neurodegenerations. In the present study, we examined the role of calpain activation and Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) degradation in DCD and excitotoxic cell death in cultured hippocampal neurons. Exposure of neurons to glutamate caused DCD accompanied by secondary mitochondrial depolarization. Activation of calpain was evidenced by detecting NCX isoform 3 (NCX3) degradation products. Degradation of NCX isoform 1 (NCX1) was below the detection limit of Western blotting. Degradation of NCX3 was detected only after 1 hr of incubation with glutamate, whereas DCD occurred on average within 15 min after glutamate application. Calpeptin, an inhibitor of calpain, significantly attenuated NCX3 degradation but failed to inhibit DCD and excitotoxic neuronal death. Calpain inhibitors I, III, and VI also failed to influence DCD and glutamate-induced neuronal death. On the other hand, MK801, an inhibitor of the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptors, added shortly after the initial glutamate-induced jump in cytosolic Ca(2+), completely prevented DCD and activation of calpain and strongly protected neurons against excitotoxicity. Taken together, our results suggest that, in glutamate-treated hippocampal neurons, the initial increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) that precedes DCD is insufficient for sustained calpain activation, which most likely occurs downstream of DCD.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Adamec E, Beermann ML, Nixon RA. Calpain I activation in rat hippocampal neurons in culture is NMDA receptor selective and not essential for excitotoxic cell death. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;54:35–48. - PubMed
-
- Araujo IM, Carreira BP, Pereira T, Santos PF, Soulet D, Inacio A, Bahr BA, Carvalho AP, Ambrosio AF, Carvalho CM. Changes in calcium dynamics following the reversal of the sodium-calcium exchanger have a key role in AMPA receptor-mediated neurodegeneration via calpain activation in hippocampal neurons. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1635–1646. - PubMed
-
- Bano D, Young KW, Guerin CJ, Lefeuvre R, Rothwell NJ, Naldini L, Rizzuto R, Carafoli E, Nicotera P. Cleavage of the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in excitotoxicity. Cell. 2005;120:275–285. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Elliott PJ, Hayward NJ, Dean RL, Harbeson S, Straub JA, Li Z, Powers JC. Calpain as a novel target for treating acute neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol Res. 1995;17:249–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

