A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial of oral selegiline hydrochloride for smoking cessation in nicotine-dependent cigarette smokers
- PMID: 19939587
- PMCID: PMC2822098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.10.009
A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial of oral selegiline hydrochloride for smoking cessation in nicotine-dependent cigarette smokers
Abstract
Aim: The primary aim of this study was to determine the safety and efficacy of the monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) inhibitor selegiline hydrochloride (SEL, l-Deprenyl; Eldepryl) as an aid for smoking cessation in cigarette smokers.
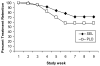
Methods: One hundred and one nicotine-dependent adult cigarette smokers without current psychiatric or substance use disorders participated in this 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Participants received either SEL (5mg bid, n=51) or placebo (PLO, n=50), in combination with brief (<10 min) manualized smoking cessation counseling. The main smoking outcome measures were 7-day point prevalence abstinence at end of trial (EOT), 4-week continuous smoking abstinence at end of trial (CA), and 7-day point prevalence abstinence at 6-month follow-up (6MFU). Abstinence was determined by an absence of self-reported cigarette smoking and biochemically verified by expired breath carbon monoxide and plasma cotinine levels.
Results: Rates of smoking abstinence did not differ by medication group (EOT: SEL=16%, PLO=20%, p=0.57; CA: SEL=14%, PLO=18%, p=0.56; 6MFU: SEL=12%, PLO=16%, p=0.54). Adverse events were modest and comparable between medication groups. Participants receiving SEL were more likely than those receiving PLO to report dry mouth (25.5% versus 8.2%, p<0.05).
Conclusions: Our results suggest that SEL was safe and well-tolerated by adult cigarette smokers, but did not improve smoking abstinence rates compared to PLO.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00129311.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Garbin MG. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: Twenty-five years of evaluation. Clin Psychol Rev. 1988;8:77–100.
-
- Benowitz NL, Jacob P, III, Ahijevich K, Jarvis MJ, Hall S, LeHouzec J, Lichenstein E, Henningfield J, Tsoh J, Hurt RD, Velicer W. Biochemical verification of tobacco use and cessation. Report from the SRNT Subcommittee on Biochemical Verification. Nicotine Tob Res. 2002;4:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Berlin I, Aubin HJ, Pedarriosse AM, Rames A, Lancrenon S, Lagrue G, Lazabemide in Smoking Cessation Study Investigators Lazabemide, a selective, reversible monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, as an aid to smoking cessation. Addiction. 2002;97:1347–1354. - PubMed
-
- Berlin I, Said S, Spreux-Varoquaux O, Launay JM, Olivares R, Millet V, Lucrubier Y, Puech AJ. A reversible monoamine oxidase A inhibitor (moclobemide) facilitates smoking cessation and abstinence in heavy, dependent smokers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1995;58:444–452. - PubMed
-
- Biberman R, Neumann R, Gerber Y. A randomized controlled trial of oral selegiline plus nicotine skin patch compared with placebo plus nicotine skin patch for smoking cessation. Addiction. 2003;98:1403–1407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical