Tpl2/AP-1 enhances murine gammaherpesvirus 68 lytic replication
- PMID: 19939924
- PMCID: PMC2812393
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01856-09
Tpl2/AP-1 enhances murine gammaherpesvirus 68 lytic replication
Abstract
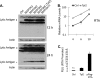
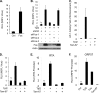
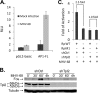
How cellular factors regulate gammaherpesvirus lytic replication is not well understood. Here, through functional screening of a cellular kinase expression library, we identified mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 (MAP3K8/Tpl2) as a positive regulator of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68 or gammaHV-68) lytic gene expression and replication. Tpl2 enhances MHV-68 lytic replication by upregulating lytic gene expression and promoter activities of viral lytic genes, including RTA and open reading frame 57 (ORF57). By screening a cellular transcription factor library, we identified the Fos AP-1 transcription factor as a downstream factor that is both necessary and sufficient for mediating the enhancement of MHV-68 lytic replication by Tpl2. In addition, Tpl2 stimulates the promoter activities of key viral lytic genes, including RTA and ORF57, in an AP-1-dependent manner. We identified an AP-1-responsive element on the MHV-68 RTA promoter as the cis element mediating the upregulation of RTA promoter activity by Tpl2. MHV-68 lytic infection upregulates Fos expression, AP-1 activity, and RTA promoter activity in a Tpl2-dependent manner. We constructed a mutant MHV-68 virus that abolished this AP-1-responsive element. This mutant virus exhibited attenuated lytic replication kinetics, indicative of a critical role of this AP-1-responsive element during lytic replication. Moreover, Tpl2 knockdown inhibited the lytic replication of wild-type MHV-68 (MHV-68-WT) but not that of the MHV-68 mutant virus, indicating that endogenous Tpl2 promotes efficient virus lytic replication through AP-1-dependent upregulation of RTA expression. In summary, through tandem functional screens, we identified the Tpl2/AP-1 signaling transduction pathway as a positive regulator of MHV-68 lytic replication.
Figures

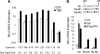
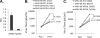
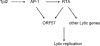
Similar articles
-
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 ORF48 Is an RTA-Responsive Gene Product and Functions in both Viral Lytic Replication and Latency during In Vivo Infection.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(11):5788-800. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00406-15. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25762743 Free PMC article.
-
Rta of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 reactivates the complete lytic cycle from latency.J Virol. 2000 Apr;74(8):3659-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.8.3659-3667.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10729142 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Rta is essential for lytic replication of murine gammaherpesvirus 68.J Virol. 2001 Oct;75(19):9262-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9262-9273.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11533188 Free PMC article.
-
Replication and transcription activator (RTA) of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 binds to an RTA-responsive element and activates the expression of ORF18.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):11338-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00561-11. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21849436 Free PMC article.
-
The Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of the gamma-herpesviridae.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:71-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089794 Review.
Cited by
-
Gammaherpesvirus gene expression and DNA synthesis are facilitated by viral protein kinase and histone variant H2AX.Virology. 2011 Nov 25;420(2):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.08.019. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21943826 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated approach to elucidate the intra-viral and viral-cellular protein interaction networks of a gamma-herpesvirus.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002297. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002297. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22028648 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress induces reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and death of primary effusion lymphoma cells.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(2):715-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01742-10. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21068240 Free PMC article.
-
A Human Gain-of-Function STING Mutation Causes Immunodeficiency and Gammaherpesvirus-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice.J Virol. 2019 Feb 5;93(4):e01806-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01806-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30463976 Free PMC article.
-
Tpl2 inhibitors thwart endothelial cell function in angiogenesis and peritoneal dissemination.Neoplasia. 2013 Sep;15(9):1036-48. doi: 10.1593/neo.121914. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 24027429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin alpha3beta1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
-
- Brass, A. L., D. M. Dykxhoorn, Y. Benita, N. Yan, A. Engelman, R. J. Xavier, J. Lieberman, and S. J. Elledge. 2008. Identification of host proteins required for HIV infection through a functional genomic screen. Science 319:921-926. - PubMed
-
- Brown, P. H., R. Alani, L. H. Preis, E. Szabo, and M. J. Birrer. 1993. Suppression of oncogene-induced transformation by a deletion mutant of c-jun. Oncogene 8:877-886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

