Protease cleavage sites in HIV-1 gp120 recognized by antigen processing enzymes are conserved and located at receptor binding sites
- PMID: 19939935
- PMCID: PMC2812349
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01765-09
Protease cleavage sites in HIV-1 gp120 recognized by antigen processing enzymes are conserved and located at receptor binding sites
Abstract
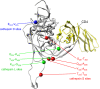
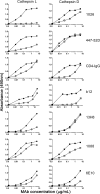
The identification of vaccine immunogens able to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) is a major goal in HIV vaccine research. Although it has been possible to produce recombinant envelope glycoproteins able to adsorb bNAbs from HIV-positive sera, immunization with these proteins has failed to elicit antibody responses effective against clinical isolates of HIV-1. Thus, the epitopes recognized by bNAbs are present on recombinant proteins, but they are not immunogenic. These results led us to consider the possibility that changes in the pattern of antigen processing might alter the immune response to the envelope glycoprotein to better elicit protective immunity. In these studies, we have defined protease cleavage sites on HIV gp120 recognized by three major human proteases (cathepsins L, S, and D) important for antigen processing and presentation. Remarkably, six of the eight sites identified in gp120 were highly conserved and clustered in regions of the molecule associated with receptor binding and/or the binding of neutralizing antibodies. These results suggested that HIV may have evolved to take advantage of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigen processing enzymes in order to evade or direct the antiviral immune response.
Figures



References
-
- Alexander-Miller, M. A., K. C. Parker, T. Tsukui, C. D. Pendleton, J. E. Coligan, and J. A. Berzofsky. 1996. Molecular analysis of presentation by HLA-A2.1 of a promiscuously binding V3 loop peptide from the HIV-envelope protein to human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 8:641-649. - PubMed
-
- Arthos, J., C. Cicala, E. Martinelli, K. Macleod, D. Van Ryk, D. Wei, Z. Xiao, T. D. Veenstra, T. P. Conrad, R. A. Lempicki, S. McLaughlin, M. Pascuccio, R. Gopaul, J. McNally, C. C. Cruz, N. Censoplano, E. Chung, K. N. Reitano, S. Kottilil, D. J. Goode, and A. S. Fauci. 2008. HIV-1 envelope protein binds to and signals through integrin alpha4beta7, the gut mucosal homing receptor for peripheral T cells. Nat. Immunol. 9:301-309. - PubMed
-
- Beddows, S., M. Franti, A. K. Dey, M. Kirschner, S. P. Iyer, D. C. Fisch, T. Ketas, E. Yuste, R. C. Desrosiers, P. J. Klasse, P. J. Maddon, W. C. Olson, and J. P. Moore. 2007. A comparative immunogenicity study in rabbits of disulfide-stabilized, proteolytically cleaved, soluble trimeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp140, trimeric cleavage-defective gp140 and monomeric gp120. Virology 360:329-340. - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., E. A. Lybarger, E. T. Crooks, M. S. Seaman, E. Gray, K. L. Davis, J. M. Decker, D. Wycuff, L. Harris, N. Hawkins, B. Wood, C. Nathe, D. Richman, G. D. Tomaras, F. Bibollet-Ruche, J. E. Robinson, L. Morris, G. M. Shaw, D. C. Montefiori, and J. R. Mascola. 2008. Profiling the specificity of neutralizing antibodies in a large panel of plasmas from patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 82:11651-11668. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., R. W. Sanders, B. Clas, N. Schuelke, A. Master, Y. Guo, F. Kajumo, D. J. Anselma, P. J. Maddon, W. C. Olson, and J. P. Moore. 2000. A recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein complex stabilized by an intermolecular disulfide bond between the gp120 and gp41 subunits is an antigenic mimic of the trimeric virion-associated structure. J. Virol. 74:627-643. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

