Characterization of a novel wood mouse virus related to murid herpesvirus 4
- PMID: 19940063
- PMCID: PMC2888160
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.017327-0
Characterization of a novel wood mouse virus related to murid herpesvirus 4
Abstract
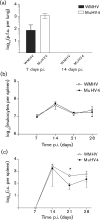
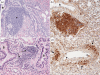
Two novel gammaherpesviruses were isolated, one from a field vole (Microtus agrestis) and the other from wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus). The genome of the latter, designated wood mouse herpesvirus (WMHV), was completely sequenced. WMHV had the same genome structure and predicted gene content as murid herpesvirus 4 (MuHV4; murine gammaherpesvirus 68). Overall nucleotide sequence identity between WMHV and MuHV4 was 85 % and most of the 10 kb region at the left end of the unique region was particularly highly conserved, especially the viral tRNA-like sequences and the coding regions of genes M1 and M4. The partial sequence (71 913 bp) of another gammaherpesvirus, Brest herpesvirus (BRHV), which was isolated ostensibly from a white-toothed shrew (Crocidura russula), was also determined. The BRHV sequence was 99.2 % identical to the corresponding portion of the WMHV genome. Thus, WMHV and BRHV appeared to be strains of a new virus species. Biological characterization of WMHV indicated that it grew with similar kinetics to MuHV4 in cell culture. The pathogenesis of WMHV in wood mice was also extremely similar to that of MuHV4, except for the absence of inducible bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue at day 14 post-infection and a higher load of latently infected cells at 21 days post-infection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epidemiology and fitness effects of wood mouse herpesvirus in a natural host population.J Gen Virol. 2012 Nov;93(Pt 11):2447-2456. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.044826-0. Epub 2012 Aug 22. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22915692 Free PMC article.
-
Partial genome analysis of murine gammaherpesvirus 4556.Acta Virol. 2012;56(3):177-86. doi: 10.4149/av_2012_03_177. Acta Virol. 2012. PMID: 23043597
-
Analysis of a novel strain of murine gammaherpesvirus reveals a genomic locus important for acute pathogenesis.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(11):5315-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5315-5327.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11333912 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine herpesvirus 4: genomic organization and relationship with two other gammaherpesviruses, Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus saimiri.Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):79-89. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01236-9. Vet Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 9011000 Review.
-
Murid herpesvirus 4 (MuHV-4, prototype strain MHV-68) as an important model in global research of human oncogenic gammaherpesviruses.Acta Virol. 2020;64(2):167-176. doi: 10.4149/av_2020_206. Acta Virol. 2020. PMID: 32551785 Review.
Cited by
-
Tick-Borne Transmission of Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Oct 31;7:458. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00458. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29164067 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Murine Herpesvirus 68 (MHV-68) in Dermacentor reticulatus Ticks.Microb Ecol. 2015 Oct;70(3):785-94. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0622-7. Epub 2015 May 8. Microb Ecol. 2015. PMID: 25947097
-
Molecular detection of murine herpesvirus 68 in ticks feeding on free-living reptiles.Microb Ecol. 2011 Nov;62(4):862-7. doi: 10.1007/s00248-011-9907-7. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Microb Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21732020
-
Gammaherpesvirus infection modulates the temporal and spatial expression of SCGB1A1 (CCSP) and BPIFA1 (SPLUNC1) in the respiratory tract.Lab Invest. 2015 Jun;95(6):610-24. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.162. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 25531566 Free PMC article.
-
First detection of murine herpesvirus 68 in adult Ixodes ricinus ticks.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018 Jul;63(4):511-515. doi: 10.1007/s12223-018-0586-3. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018. PMID: 29352410
References
-
- Bell, M. J., Brennan, R., Miles, J. J., Moss, D. J., Burrows, J. M. & Burrows, S. R. (2008). Widespread sequence variation in Epstein–Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 influences the antiviral T cell response. J Infect Dis 197, 1594–1597. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, M., Crouch, A. J., Begon, M., Duffy, B., Feore, S., Gaskell, R. M., Kelly, D. F., McCracken, C. M., Vicary, L. & Baxby, D. (1997). Cowpox in British voles and mice. J Comp Pathol 116, 35–44. - PubMed
-
- Blasdell, K., McCracken, C., Morris, A., Nash, A. A., Begon, M., Bennett, M. & Stewart, J. P. (2003). The wood mouse is a natural host for Murid herpesvirus 4. J Gen Virol 84, 111–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

