Protein-protein interaction between cPLA2 and splice variants of alpha-subunit of BK channels
- PMID: 19940072
- PMCID: PMC3774341
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00221.2009
Protein-protein interaction between cPLA2 and splice variants of alpha-subunit of BK channels
Abstract
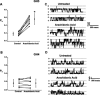
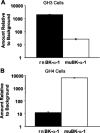
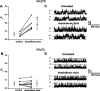
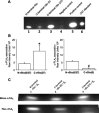
Altering the splice variant composition of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated potassium (BK) channels can alter their activity and apparent sensitivity to Ca(2+) and other regulators of activity. We hypothesized that differences in the responsiveness to arachidonic acid of GH3 and GH4 cells was due to a difference in two splice variants, one present in GH3 cells and the other in GH4 cells. The sequences of the two splice variants differ from one another in several ways, but the largest difference is the presence or absence of 27 amino acids in the COOH terminus of the BK alpha-subunit. Open probability of the variant containing the 27 amino acids is significantly increased by arachidonic acid, while the variant lacking the 27 amino acids is insensitive to arachidonic acid. In addition, sensitivity of BK channels to arachidonic acid depends on cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)). Here we used the Mammalian Matchmaker two-hybrid assay and two BK alpha-subunit constructs with [rSlo(27)] and without [rSlo(0)] the 27-amino acid motif to determine whether cPLA(2) associates with one construct [rSlo(27)] and not the other. We hypothesized that differential association of cPLA(2) might explain the differing responsiveness of the two constructs and GH3 and GH4 cells to arachidonic acid. We found that cPLA(2) is strongly associated with the COOH terminus of rSlo(27) and only very weakly associated with rSlo(0). We also found that arachidonic acid has a lower affinity for rSlo(0) than for rSlo(27). We conclude that the lack of response of BK channels in GH4 cells to arachidonic acid can be explained, in part, by the poor binding of cPLA(2) to the COOH terminus of the rSlo(0) alpha-subunit, which is very similar to the splice variant found in the arachidonic acid-insensitive GH4 cells.
Figures





References
-
- Brenner R, Jegla TJ, Wickenden A, Liu Y, Aldrich RW. Cloning and functional characterization of novel large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunits, hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4. J Biol Chem 275: 6453–6461, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Denson DD, Li J, Eaton DC. Co-localization of the alpha-subunit of BK-channels and c-PLA2 in GH3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350: 39–49, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Denson DD, Wang X, Worrell RT, AlKhalili O, Eaton DC. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is required for optimal ATP activation of BK channels in GH3 cells. J Biol Chem 276: 7136–7142, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Denson DD, Wang X, Worrell RT, Eaton DC. Effects of fatty acids on BK channels in GH3 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279: C1211–C1219, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

