Resveratrol (trans-3,5,4'-trihydroxystilbene) induces silent mating type information regulation-1 and down-regulates nuclear transcription factor-kappaB activation to abrogate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
- PMID: 19940103
- PMCID: PMC2835444
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.160838
Resveratrol (trans-3,5,4'-trihydroxystilbene) induces silent mating type information regulation-1 and down-regulates nuclear transcription factor-kappaB activation to abrogate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
Abstract
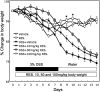
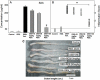
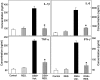
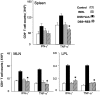
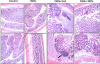
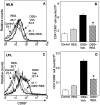
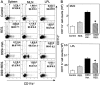
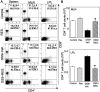
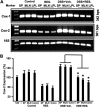
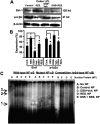
Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic, relapsing, and tissue-destructive disease. Resveratrol (3,4,5-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene), a naturally occurring polyphenol that exhibits beneficial pleiotropic health effects, is recognized as one of the most promising natural molecules in the prevention and treatment of chronic inflammatory disease and autoimmune disorders. In the present study, we investigated the effect of resveratrol on dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in mice and found that it effectively attenuated overall clinical scores as well as various pathological markers of colitis. Resveratrol reversed the colitis-associated decrease in body weight and increased levels of serum amyloid A, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL-6), and IL-1beta. After resveratrol treatment, the percentage of CD4(+) T cells in mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) of colitis mice was restored to normal levels, and there was a decrease in these cells in the colon lamina propria (LP). Likewise, the percentages of macrophages in MLN and the LP of mice with colitis were decreased after resveratrol treatment. Resveratrol also suppressed cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression induced in DSS-exposed mice. Colitis was associated with a decrease in silent mating type information regulation-1 (SIRT1) gene expression and an increase in p-inhibitory kappaB expression and nuclear transcription factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation. Resveratrol treatment of mice with colitis significantly reversed these changes. This study demonstrates for the first time that SIRT1 is involved in colitis, functioning as an inverse regulator of NF-kappaB activation and inflammation. Furthermore, our results indicate that resveratrol may protect against colitis through up-regulation of SIRT1 in immune cells in the colon.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol and piceatannol inhibit iNOS expression and NF-kappaB activation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mouse colitis.Nutr Cancer. 2009;61(6):847-54. doi: 10.1080/01635580903285072. Nutr Cancer. 2009. PMID: 20155626
-
Role of microRNAs in resveratrol-mediated mitigation of colitis-associated tumorigenesis in Apc(Min/+) mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Jul;350(1):99-109. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.213306. Epub 2014 May 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24817032 Free PMC article.
-
FGL2 regulates IKK/NF-κB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and lamina propria dendritic cells to attenuate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.Mol Immunol. 2020 Jan;117:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.11.001. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31743856
-
Role of resveratrol-induced CD11b(+) Gr-1(+) myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the reduction of CXCR3(+) T cells and amelioration of chronic colitis in IL-10(-/-) mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Jan;26(1):72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.07.236. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 21807089 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcodon aspratus Extract Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mouse Colon and Mesenteric Lymph Nodes.J Food Sci. 2016 May;81(5):H1301-8. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13297. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Food Sci. 2016. PMID: 27074537
Cited by
-
Resveratrol improves cardiac contractility following trauma-hemorrhage by modulating Sirt1.Mol Med. 2012 Mar 27;18(1):209-14. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00365. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22113495 Free PMC article.
-
Interventional effects of plumbagin on experimental ulcerative colitis in mice.J Nat Prod. 2013 Jun 28;76(6):1001-6. doi: 10.1021/np3008792. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Nat Prod. 2013. PMID: 23742275 Free PMC article.
-
Tetradecylthioacetic acid attenuates inflammation and has antioxidative potential during experimental colitis in rats.Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Jan;58(1):97-106. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2321-2. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 22855292
-
Evolving Interplay Between Dietary Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota-An Emerging Importance in Healthcare.Front Nutr. 2021 May 24;8:634944. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.634944. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34109202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Food-Derived Bioactive Compounds on Intestinal Immunity.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 18;11(12):1901. doi: 10.3390/biom11121901. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhat KP, Pezzuto JM. (2001) Resveratrol exhibits cytostatic and antiestrogenic properties with human endometrial adenocarcinoma (Ishikawa) cells. Cancer Res 61:6137–6144 - PubMed
-
- Birrell MA, McCluskie K, Wong S, Donnelly LE, Barnes PJ, Belvisi MG. (2005) Resveratrol, an extract of red wine, inhibits lipopolysaccharide induced airway neutrophilia and inflammatory mediators through an NF-κB-independent mechanism. FASEB J 19:840–841 - PubMed
-
- Blander G, Guarente L. (2004) The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem 73:417–435 - PubMed
-
- Casini-Raggi V, Kam L, Chong YJ, Fiocchi C, Pizarro TT, Cominelli F. (1995) Mucosal imbalance of IL-1 and IL-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease. A novel mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation. J Immunol 154:2434–2440 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

