Chromatin remodeling by imitation switch (ISWI) class ATP-dependent remodelers is stimulated by histone variant H2A.Z
- PMID: 19940112
- PMCID: PMC2836070
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.072348
Chromatin remodeling by imitation switch (ISWI) class ATP-dependent remodelers is stimulated by histone variant H2A.Z
Abstract
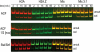
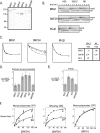
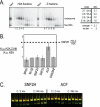
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes rearrange nucleosomes by altering the position of DNA around the histone octamer. Although chromatin remodelers and the histone variant H2A.Z colocalize on transcriptional control regions, whether H2A.Z directly affects remodeler association or activity is unclear. We determined the relative association of remodelers with H2A.Z chromatin and tested whether replacement of H2A.Z in a nucleosome altered the activity of remodeling enzymes. Many families of remodelers showed increased association with H2A.Z chromatin, but only the ISWI family of chromatin remodelers showed stimulated activity in vitro. An acidic patch on the nucleosome surface, extended by inclusion of H2A.Z in nucleosomes and essential for viability, is required for ISWI stimulation. We conclude that H2A.Z incorporation increases nucleosome remodeling activity of the largest class of mammalian remodelers (ISWI) and that it correlates with increased association of other remodelers to chromatin. This reveals two possible modes for regulation of a remodeler by a histone variant.
Figures

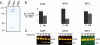
Similar articles
-
Kinetic control of nucleosome displacement by ISWI/ACF chromatin remodelers.Phys Rev Lett. 2012 Sep 14;109(11):118103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.118103. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Phys Rev Lett. 2012. PMID: 23005680
-
Variation on a theme: Evolutionary strategies for H2A.Z exchange by SWR1-type remodelers.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021 Jun;70:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.10.014. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33217681 Review.
-
NuA4-dependent acetylation of nucleosomal histones H4 and H2A directly stimulates incorporation of H2A.Z by the SWR1 complex.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):15966-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.117069. Epub 2010 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20332092 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Octamer Structure Is Altered Early in ISW2 ATP-Dependent Nucleosome Remodeling.Cell Rep. 2019 Jul 2;28(1):282-294.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.106. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31269447
-
Mechanisms for nucleosome movement by ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;41:127-48. doi: 10.1007/400_005. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 16909894 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone variants: dynamic punctuation in transcription.Genes Dev. 2014 Apr 1;28(7):672-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.238873.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24696452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TbISWI regulates multiple polymerase I (Pol I)-transcribed loci and is present at Pol II transcription boundaries in Trypanosoma brucei.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Jul;10(7):964-76. doi: 10.1128/EC.05048-11. Epub 2011 May 13. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 21571922 Free PMC article.
-
The variant histone H2A.V of Drosophila--three roles, two guises.Chromosoma. 2013 Aug;122(4):245-58. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0409-x. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Chromosoma. 2013. PMID: 23553272 Review.
-
Histone H2A variants in nucleosomes and chromatin: more or less stable?Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov;40(21):10719-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks865. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23002134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone variants at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2021 Mar 26;134(6):jcs244749. doi: 10.1242/jcs.244749. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 33771851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

