The C53/C37 subcomplex of RNA polymerase III lies near the active site and participates in promoter opening
- PMID: 19940126
- PMCID: PMC2807326
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074013
The C53/C37 subcomplex of RNA polymerase III lies near the active site and participates in promoter opening
Abstract
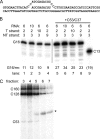
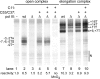
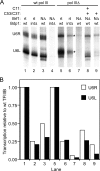
The C53 and C37 subunits of RNA polymerase III (pol III) form a subassembly that is required for efficient termination; pol III lacking this subcomplex displays increased processivity of RNA chain elongation. We show that the C53/C37 subcomplex additionally plays a role in formation of the initiation-ready open promoter complex similar to that of the Brf1 N-terminal zinc ribbon domain. In the absence of C53 and C37, the transcription bubble fails to stably propagate to and beyond the transcriptional start site even when the DNA template is supercoiled. The C53/C37 subcomplex also stimulates the formation of an artificially assembled elongation complex from its component DNA and RNA strands. Protein-RNA and protein-DNA photochemical cross-linking analysis places a segment of C53 close to the RNA 3' end and transcribed DNA strand at the catalytic center of the pol III elongation complex. We discuss the implications of these findings for the mechanism of transcriptional termination by pol III and propose a structural as well as functional correspondence between the C53/C37 subcomplex and the RNA polymerase II initiation factor TFIIF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A subcomplex of RNA polymerase III subunits involved in transcription termination and reinitiation.EMBO J. 2006 Jan 11;25(1):118-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600915. Epub 2005 Dec 15. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16362040 Free PMC article.
-
The TFIIF-like Rpc37/53 dimer lies at the center of a protein network to connect TFIIIC, Bdp1, and the RNA polymerase III active center.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;31(13):2715-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05151-11. Epub 2011 May 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21536656 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishing core and holoenzyme mechanisms of transcription termination by RNA polymerase III.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;33(8):1571-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01733-12. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23401852 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription termination by the eukaryotic RNA polymerase III.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):318-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23099421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide RNA polymerase II: not genes only!Trends Biochem Sci. 2008 Jun;33(6):265-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 May 6. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008. PMID: 18467100 Review.
Cited by
-
A mutation in POLR3E impairs antiviral immune response and RNA polymerase III.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):22113-22121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009947117. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32843346 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pol III transcription by nutrient and stress signaling pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):361-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23165150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal structure of the C17/25 subcomplex from Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA polymerase III.Protein Sci. 2011 Sep;20(9):1558-65. doi: 10.1002/pro.682. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Protein Sci. 2011. PMID: 21714024 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into transcriptional regulation of human RNA polymerase III.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;28(2):220-227. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00557-x. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33558766
-
A methods review on use of nonsense suppression to study 3' end formation and other aspects of tRNA biogenesis.Gene. 2015 Feb 1;556(1):35-50. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.034. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25447915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dieci G., Fiorino G., Castelnuovo M., Teichmann M., Pagano A. (2007) Trends Genet. 23, 614–622 - PubMed
-
- Schramm L., Hernandez N. (2002) Genes Dev. 16, 2593–2620 - PubMed
-
- Geiduschek E. P., Kassavetis G. A. (2001) J. Mol. Biol. 310, 1–26 - PubMed
-
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. (1990) Cell 60, 235–245 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

