Plasmodium falciparum BAEBL binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans on the human erythrocyte surface
- PMID: 19940142
- PMCID: PMC2804329
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.021576
Plasmodium falciparum BAEBL binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans on the human erythrocyte surface
Abstract
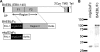
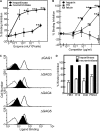
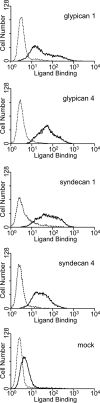
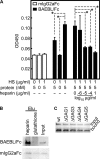
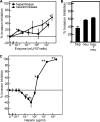
Erythrocyte invasion is critical to the pathogenesis and survival of the malarial parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. This process is partly mediated by proteins that belong to the Duffy binding-like family, which are expressed on the merozoite surface. One of these proteins, BAEBL (also known as EBA-140), is thought to bind to glycophorin C in a sialic acid-dependent manner. In this report, by the binding assay between recombinant BAEBL protein and enzyme-treated erythrocytes, we show that the binding of BAEBL to erythrocytes is mediated primarily by sialic acid and partially through heparan sulfate (HS). Because BAEBL binds to several kinds of HS proteoglycans or purified HS, the BAEBL-HS binding was found to be independent of the HS proteoglycan peptide backbone and the presence of sialic acid moieties. Furthermore, both the sialic acid- and HS-dependent binding were disrupted by the addition of soluble heparin. This inhibition may be the result of binding between BAEBL and heparin. Invasion assays demonstrated that HS-dependent binding was related to the efficiency of merozoite invasion. These results suggest that HS functions as a factor that promotes the binding of BAEBL and merozoite invasion. Moreover, these findings may explain the invasion inhibition mechanisms observed following the addition of heparin and other sulfated glycoconjugates.
Figures
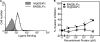

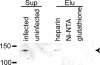
References
-
- Dvorak J. A., Miller L. H., Whitehouse W. C., Shiroishi T. (1975) Science 187, 748–750 - PubMed
-
- Adams J. H., Blair P. L., Kaneko O., Peterson D. S. (2001) Trends Parasitol. 17, 297–299 - PubMed
-
- Sim B. K., Chitnis C. E., Wasniowska K., Hadley T. J., Miller L. H. (1994) Science 264, 1941–1944 - PubMed
-
- Pasvol G. (2003) Trends Parasitol. 19, 430–432 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

