Structural determinants of the high affinity extracellular zinc binding site on Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels
- PMID: 19940152
- PMCID: PMC2823403
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.067660
Structural determinants of the high affinity extracellular zinc binding site on Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels
Abstract
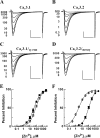
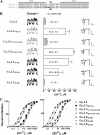
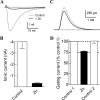
Ca(v)3.2 T-type channels contain a high affinity metal binding site for trace metals such as copper and zinc. This site is occupied at physiologically relevant concentrations of these metals, leading to decreased channel activity and pain transmission. A histidine at position 191 was recently identified as a critical determinant for both trace metal block of Ca(v)3.2 and modulation by redox agents. His(191) is found on the extracellular face of the Ca(v)3.2 channel on the IS3-S4 linker and is not conserved in other Ca(v)3 channels. Mutation of the corresponding residue in Ca(v)3.1 to histidine, Gln(172), significantly enhances trace metal inhibition, but not to the level observed in wild-type Ca(v)3.2, implying that other residues also contribute to the metal binding site. The goal of the present study is to identify these other residues using a series of chimeric channels. The key findings of the study are that the metal binding site is composed of a Asp-Gly-His motif in IS3-S4 and a second aspartate residue in IS2. These results suggest that metal binding stabilizes the closed conformation of the voltage-sensor paddle in repeat I, and thereby inhibits channel opening. These studies provide insight into the structure of T-type channels, and identify an extracellular motif that could be targeted for drug development.
Figures


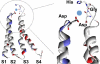
Similar articles
-
Complex modulation of Ca(v)3.1 T-type calcium channel by nickel.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 May;70(9):1653-61. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1225-9. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23250353 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating an extracellular redox-sensitive module in T-type Ca2+ channels.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 1;295(18):6177-6186. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012668. Epub 2020 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32188693 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular determinant of nickel inhibition in Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 24;281(8):4823-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510197200. Epub 2005 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16377633
-
T-type calcium channel blockers - new and notable.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2011 Dec;30(4):403-9. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2011_04_403. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2011. PMID: 22131323 Review.
-
Models of calcium permeation through T-type channels.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Apr;466(4):635-44. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1437-3. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24449276 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex modulation of Ca(v)3.1 T-type calcium channel by nickel.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 May;70(9):1653-61. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1225-9. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23250353 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating an extracellular redox-sensitive module in T-type Ca2+ channels.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 1;295(18):6177-6186. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012668. Epub 2020 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32188693 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-Dependent Modulation of T-Type Ca(2+) Channels in Sensory Neurons Contributes to Acute Anti-Nociceptive Effect of Substance P.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Aug 10;25(5):233-51. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6560. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 27306612 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Znt8 function in diabetes mellitus: risk or benefit?Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jul;476(7):2703-2718. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04114-4. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33666829 Review.
-
T-type voltage-gated calcium channels as targets for the development of novel pain therapies.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;163(3):484-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01256.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21306582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perez-Reyes E. (2003) Physiol. Rev. 83, 117–161 - PubMed
-
- Iftinca M. C., Zamponi G. W. (2009) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 30, 32–40 - PubMed
-
- Kozlov A. S., McKenna F., Lee J. H., Cribbs L. L., Perez-Reyes E., Feltz A., Lambert R. C. (1999) Eur. J. Neurosci. 11, 4149–4158 - PubMed
-
- Ellinor P. T., Yang J., Sather W. A., Zhang J. F., Tsien R. W. (1995) Neuron 15, 1121–1132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

