Adenosine A2A receptor blockade prevents synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction caused by beta-amyloid peptides via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- PMID: 19940169
- PMCID: PMC6665997
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3728-09.2009
Adenosine A2A receptor blockade prevents synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction caused by beta-amyloid peptides via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Abstract
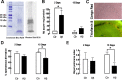
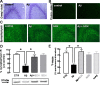
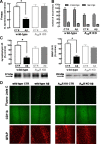
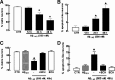
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by memory impairment, neurochemically by accumulation of beta-amyloid peptide (namely Abeta(1-42)) and morphologically by an initial loss of nerve terminals. Caffeine consumption prevents memory dysfunction in different models, which is mimicked by antagonists of adenosine A(2A) receptors (A(2A)Rs), which are located in synapses. Thus, we now tested whether A(2A)R blockade prevents the early Abeta(1-42)-induced synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction and what are the underlying signaling pathways. The intracerebral administration of soluble Abeta(1-42) (2 nmol) in rats or mice caused, 2 weeks later, memory impairment (decreased performance in the Y-maze and object recognition tests) and a loss of nerve terminal markers (synaptophysin, SNAP-25) without overt neuronal loss, astrogliosis, or microgliosis. These were prevented by pharmacological blockade [5-amino-7-(2-phenylethyl)-2-(2-furyl)-pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine (SCH58261); 0.05 mg . kg(-1) . d(-1), i.p.; for 15 d] in rats, and genetic inactivation of A(2A)Rs in mice. Moreover, these were synaptic events since purified nerve terminals acutely exposed to Abeta(1-42) (500 nm) displayed mitochondrial dysfunction, which was prevented by A(2A)R blockade. SCH58261 (50 nm) also prevented the initial synaptotoxicity (loss of MAP-2, synaptophysin, and SNAP-25 immunoreactivity) and subsequent loss of viability of cultured hippocampal neurons exposed to Abeta(1-42) (500 nm). This A(2A)R-mediated control of neurotoxicity involved the control of Abeta(1-42)-induced p38 phosphorylation and was independent from cAMP/PKA (protein kinase A) pathway. Together, these results show that A(2A)Rs play a crucial role in the development of Abeta-induced synaptotoxicity leading to memory dysfunction through a p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase)-dependent pathway and provide a molecular basis for the benefits of caffeine consumption in AD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Astrocytic adenosine A2A receptors control the amyloid-β peptide-induced decrease of glutamate uptake.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;31(3):555-67. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120469. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22647260
-
Caffeine and adenosine A(2a) receptor antagonists prevent beta-amyloid (25-35)-induced cognitive deficits in mice.Exp Neurol. 2007 Jan;203(1):241-5. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.08.008. Epub 2006 Sep 27. Exp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17007839
-
Blockade of adenosine A2A receptors prevents interleukin-1β-induced exacerbation of neuronal toxicity through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Aug 20;9:204. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-204. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22901528 Free PMC article.
-
A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(24):4138-4151. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666211129122550. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34844537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease: Rouge of brain kinases.Brain Res Bull. 2025 May;224:111296. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111296. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 40073950 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of death-associated protein kinase 1 attenuates cis P-tau and neurodegeneration in traumatic brain injury.Prog Neurobiol. 2021 Aug;203:102072. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102072. Epub 2021 May 9. Prog Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33979671 Free PMC article.
-
Development of 18F-Labeled Radiotracers for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor: Synthesis, Radiolabeling and Preliminary Biological Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2285. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052285. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669003 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting adenosine A2A receptors for early intervention of retinopathy of prematurity.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Feb 8. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-09986-x. Online ahead of print. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38329708 Review.
-
Anthocyanins control neuroinflammation and consequent memory dysfunction in mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;54(5):3350-3367. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9900-8. Epub 2016 May 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27167130
-
Impact of Coffee Intake on Measures of Wellbeing in Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 1;16(17):2920. doi: 10.3390/nu16172920. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angulo E, Casadó V, Mallol J, Canela EI, Viñals F, Ferrer I, Lluis C, Franco R. A1 adenosine receptors accumulate in neurodegenerative structures in Alzheimer disease and mediate both amyloid precursor protein processing and tau phosphorylation and translocation. Brain Pathol. 2003;13:440–451. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arendash GW, Schleif W, Rezai-Zadeh K, Jackson EK, Zacharia LC, Cracchiolo JR, Shippy D, Tan J. Caffeine protects Alzheimer's mice against cognitive impairment and reduces brain beta-amyloid production. Neuroscience. 2006;142:941–952. - PubMed
-
- Arias C, Montiel T, Quiroz-Báez R, Massieu L. β-Amyloid neurotoxicity is exacerbated during glycolysis inhibition and mitochondrial impairment in the rat hippocampus in vivo and in isolated nerve terminals: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Exp Neurol. 2002;176:163–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
