PACAP neurons in the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus are targets of central leptin signaling
- PMID: 19940178
- PMCID: PMC6666015
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1526-09.2009
PACAP neurons in the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus are targets of central leptin signaling
Abstract
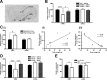
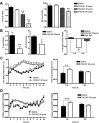
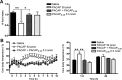
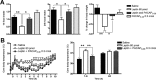
The adipose-derived hormone, leptin, was discovered over 10 years ago, but only now are we unmasking its downstream pathways which lead to reduced energy intake (feeding) and increased energy expenditure (thermogenesis). Recent transgenic models have challenged the long-standing supposition that the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (Arc) is omnipotent in the central response to leptin, and research focus is beginning to shift to examine roles of extra-arcuate sites. Dhillon et al. (2006) demonstrated that targeted knock out of the signaling form of the leptin receptor (lepr-B) in steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) cells of the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus (VMN) produces obesity of a similar magnitude to the pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)-driven lepr-B deleted mouse, via a functionally distinct mechanism. These findings reveal that SF-1 cells of the VMN could be equally as important as POMC cells in mediating leptin's anti-obesity effects. However, the identification of molecular and cellular correlates of this relationship remains tantalizingly unknown. Here, we have shown that mRNA expression of the VMN-expressed neuropeptide pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is regulated according to energy status and that it exerts catabolic effects when administered centrally to mice. Furthermore, we have shown that SF-1 and PACAP mRNAs are colocalized in the VMN, and that leptin signaling via lepr-B is required for normal PACAP expression in these cells. Finally, blocking endogenous central PACAP signaling with the antagonist PACAP(6-38) markedly attenuates leptin-induced hypophagia and hyperthermia in vivo. Thus, it appears that PACAP is an important mediator of central leptin effects on energy balance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus subset stimulates tissue thermogenesis via preoptic area outputs.Mol Metab. 2024 Jun;84:101951. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101951. Epub 2024 May 8. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38729241 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of the hypothalamic ventromedial nuclei by pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide induces hypophagia and thermogenesis.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):R1625-34. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00334.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21957159 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Blockade of PACAP-Dependent Activity in the Ventromedial Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Disrupts Leptin-Induced Behavioral and Molecular Changes in Rats.Neuroendocrinology. 2020;110(3-4):271-281. doi: 10.1159/000501337. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Neuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31167202 Free PMC article.
-
The PACAP Paradox: Dynamic and Surprisingly Pleiotropic Actions in the Central Regulation of Energy Homeostasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 1;13:877647. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.877647. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PACAP in the Defense of Energy Homeostasis.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Sep;27(9):620-632. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 May 8. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27166671 Review.
Cited by
-
Leptin signaling and its central role in energy homeostasis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 31;17:1238528. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1238528. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38027481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parabrachial-to-parasubthalamic nucleus pathway mediates fear-induced suppression of feeding in male mice.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 30;13(1):7913. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35634-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36585411 Free PMC article.
-
Central Control of Feeding Behavior by the Secretin, PACAP, and Glucagon Family of Peptides.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Feb 7;8:18. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00018. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28223965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anorexigenic neuropeptides as anti-obesity and neuroprotective agents: exploring the neuroprotective effects of anorexigenic neuropeptides.Biosci Rep. 2024 Apr 24;44(4):BSR20231385. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231385. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38577975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus subset stimulates tissue thermogenesis via preoptic area outputs.Mol Metab. 2024 Jun;84:101951. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101951. Epub 2024 May 8. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38729241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antin J, Gibbs J, Holt J, Young RC, Smith GP. Cholecystokinin elicits the complete behavioral sequence of satiety in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1975;89:784–790. - PubMed
-
- Archer ZA, Rayner DV, Rozman J, Klingenspor M, Mercer JG. Normal distribution of body weight gain in male Sprague-Dawley rats fed a high-energy diet. Obes Res. 2003;11:1376–1383. - PubMed
-
- Arimura A. Impaired adaptive thermogenesis in pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-deficient mice. Endocrinology. 2002;143:3715–3716. - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, Coppari R, McMinn J, Liu SM, Lee CE, Tang V, Kenny CD, McGovern RA, Chua SC, Jr, Elmquist JK, Lowell BB. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2004;42:983–991. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold DA, Brown TM, Luckman SM, Piggins HD. Metabolic rhythm abnormalities in mice lacking VIP-VPAC2 signaling. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;294:R344–R351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
