Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostacyclin formation and blood pressure homeostasis: targeted exchange of cyclooxygenase isoforms in mice
- PMID: 19940265
- PMCID: PMC2818801
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.204529
Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostacyclin formation and blood pressure homeostasis: targeted exchange of cyclooxygenase isoforms in mice
Erratum in
- Circ Res. 2010 Nov 12;107(10):e19. Symth, Emer M [corrected to Smyth, Emer M]
Abstract
Rationale: Cyclooxygenase (COX)-derived prostanoids (PGs) are involved in blood pressure homeostasis. Both traditional nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 and NSAIDs designed to be selective for inhibition of COX-2 cause sodium retention and elevate blood pressure.
Objective: To elucidate the role of COX-2 in blood pressure homeostasis using COX-1>COX-2 mice, in which the COX-1 expression is controlled by COX-2 regulatory elements.
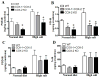
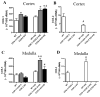
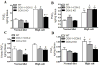
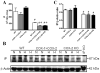
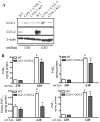
Methods and results: COX-1>COX-2 mice developed systolic hypertension relative to wild types (WTs) on a high-salt diet (HSD); this was attenuated by a PGI(2) receptor agonist. HSD increased expression of COX-2 in WT mice and of COX-1 in COX-1>COX-2 mice in the inner renal medulla. The HSD augmented in all strains urinary prostanoid metabolite excretion, with the exception of the major PGI(2) metabolite that was suppressed on regular chow and unaltered by the HSD in both mutants. Furthermore, inner renal medullary expression of the receptor for PGI(2), but not for other prostanoids, was depressed by HSD in WT and even more so in both mutant strains. Increasing osmolarity augmented expression of COX-2 in WT renal medullary interstitial cells and again the increase in formation of PGI(2) observed in WTs was suppressed in cells derived from both mutants. Intramedullary infusion of the PGI(2) receptor agonist increased urine volume and sodium excretion in mice.
Conclusions: These studies suggest that dysregulated expression of the COX-2 dependent, PGI(2) biosynthesis/response pathway in the renal inner renal medulla undermines the homeostatic response to a HSD. Inhibition of this pathway may contribute directly to the hypertensive response to NSAIDs.
Figures
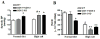
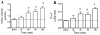
Similar articles
-
Vascular COX-2 modulates blood pressure and thrombosis in mice.Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 2;4(132):132ra54. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003787. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22553252 Free PMC article.
-
Increased dietary NaCl induces renal medullary PGE2 production and natriuresis via the EP2 receptor.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):F818-25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90253.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18632796 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Medullary Interstitial COX-2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) Is Essential in Preventing Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Maintaining Renal Inner Medulla/Papilla Structural Integrity.Hypertension. 2018 Nov;72(5):1172-1179. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11694. Hypertension. 2018. PMID: 30354807 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of renal medullary cyclooxygenase-2 during high salt loading.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017 Jan 1;22(1):128-136. doi: 10.2741/4476. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017. PMID: 27814606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition and renal physiology.Am J Cardiol. 2002 Mar 21;89(6A):10D-17D. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(02)02232-4. Am J Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 11909556 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic and lipidomic analyses differentiate the compensatory roles of two COX isoforms during systemic inflammation in mice.J Lipid Res. 2018 Jan;59(1):102-112. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M080028. Epub 2017 Nov 27. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29180443 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-1 deletion in 5 × FAD mice protects against microglia-induced neuroinflammation and mitigates cognitive impairment.Transl Neurodegener. 2025 Aug 22;14(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40035-025-00501-9. Transl Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40847374 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular cAMP-adenosine pathways in the mouse kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):F565-73. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00094.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21653635 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 Modulates Glycosaminoglycan Production in the Skin During Salt Overload.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 23;11:561722. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.561722. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33192558 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular COX-2 modulates blood pressure and thrombosis in mice.Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 2;4(132):132ra54. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003787. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22553252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith WL, DeWitt DL, Garavito RM. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:145–182. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong EP, Malone DC. The impact of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on blood pressure, with an emphasis on newer agents. Clin Ther. 2003;25:1–18. - PubMed
-
- FitzGerald GA. COX-2 and beyond: Approaches to prostaglandin inhibition in human disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:879–890. - PubMed
-
- Fujino T, Nakagawa N, Yuhki K, Hara A, Yamada T, Takayama K, Kuriyama S, Hosoki Y, Takahata O, Taniguchi T, Fukuzawa J, Hasebe N, Kikuchi K, Narumiya S, Ushikubi F. Decreased susceptibility to renovascular hypertension in mice lacking the prostaglandin I2 receptor IP. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:805–812. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whelton A, White WB, Bello AE, Puma JA, Fort JG. Effects of celecoxib and rofecoxib on blood pressure and edema in patients > or =65 years of age with systemic hypertension and osteoarthritis. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:959–963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

