25-Hydroxyvitamin D, dementia, and cerebrovascular pathology in elders receiving home services
- PMID: 19940273
- PMCID: PMC2809024
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181beecb7
25-Hydroxyvitamin D, dementia, and cerebrovascular pathology in elders receiving home services
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D deficiency has potential adverse effects on neurocognitive health and subcortical function. However, no studies have examined the association between vitamin D status, dementia, and cranial MRI indicators of cerebrovascular disease (CVD).
Methods: Cross-sectional investigation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D], dementia, and MRI measures of CVD in elders receiving home care (aged 65-99 years) from 2003 to 2007.
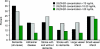
Results: Among 318 participants, the mean age was 73.5 +/- 8.1 years, 231 (72.6%) were women, and 109 (34.3%) were black. 25(OH)D concentrations were deficient (<10 ng/mL) in 14.5% and insufficient (10-20 ng/mL) in 44.3% of participants. There were 76 participants (23.9%) with dementia, 41 of which were classified as probable AD. Mean 25(OH)D concentrations were lower in subjects with dementia (16.8 vs 20.0 ng/mL, p < 0.01). There was a higher prevalence of dementia among participants with 25(OH)D insufficiency (< or =20 ng/mL) (30.5% vs 14.5%, p < 0.01). 25(OH)D deficiency was associated with increased white matter hyperintensity volume (4.9 vs 2.9 mL, p < 0.01), grade (3.0 vs 2.2, p = 0.04), and prevalence of large vessel infarcts (10.1% vs 6.9%, p < 0.01). After adjustment for age, race, sex, body mass index, and education, 25(OH)D insufficiency (< or =20 ng/mL) was associated with more than twice the odds of all-cause dementia (odds ratio [OR] = 2.3, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.2-4.2), Alzheimer disease (OR = 2.5, 95% CI 1.1-6.1), and stroke (with and without dementia symptoms) (OR = 2.0, 95% CI 1.0-4.0).
Conclusions: Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency was associated with all-cause dementia, Alzheimer disease, stroke (with and without dementia symptoms), and MRI indicators of cerebrovascular disease. These findings suggest a potential vasculoprotective role of vitamin D.
Figures
Comment in
-
25-hydroxyvitamin D, dementia, and cerebrovascular pathology in elders receiving home services.Neurology. 2010 Jul 6;75(1):95; author reply 95-6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e00ddb. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 20603493 No abstract available.
References
-
- Roman GC. Stroke, cognitive decline and vascular dementia: the silent epidemic of the 21st century. Neuroepidemiology 2003;22:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Vermeer SE, Hollander M, van Dijk EJ, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM. Silent brain infarcts and white matter lesions increase stroke risk in the general population: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Stroke 2003;34:1126–1129. - PubMed
-
- Snowdon DA, Greiner LH, Mortimer JA, Riley KP, Greiner PA, Markesbery WR. Brain infarction and the clinical expression of Alzheimer disease: The Nun Study. JAMA 1997;277:813–817. - PubMed
-
- Vermeer SE, Prins ND, den Heijer T, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM. Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1215–1222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG02707087-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076092-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS059933/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR053205/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL54776/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG023394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG21790/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 DK69341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK064902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR41398/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG021790/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051361-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R13DK069541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R13 DK069541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R0I DK79003/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK071636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK071636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR052322-0121/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AT003714-01/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR052322-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG027087A/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK78867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical