Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by FTY720 is neuroprotective after ischemic stroke in rats
- PMID: 19940275
- PMCID: PMC2811754
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.568899
Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by FTY720 is neuroprotective after ischemic stroke in rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: FTY720 is a known sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist. In the present study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of postischemic administration of FTY720 in rats with 2 hours transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO).
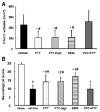
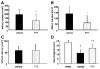
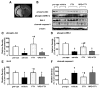
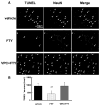
Methods: One hundred eleven male rats were randomly assigned to sham-operated and MCAO treated with vehicle, 0.25 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg of FTY720, another selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 agonist SEW2871 (5 mg/kg), or 0.25 mg/kg of FTY720 plus a sphingosine 1-phosphate antagonist, VPC23019 (0.5 mg/kg). Drugs were injected intraperitoneally immediately after reperfusion. Neurological score and infarct volume were assessed at 24 and 72 hours after MCAO. Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated uridine 5'-triphosphate-biotin nick end-labeling were conducted at 24 hours after MCAO.
Results: FTY720 significantly reduced infarct volume and improved neurological score at 24 and 72 hours after MCAO compared with the vehicle group. SEW2871 showed similar neuroprotective effects to FTY720, whereas VPC 20319 abolished the neuroprotective effects of FTY720. FTY720 significantly retained Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation and Bcl-2 expression and decreased cleaved caspase-3 expression and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated uridine 5'-triphosphate-biotin nick end-labeling-positive neurons at 24 hours after MCAO. VPC23019 blocked the antiapoptotic effects of FTY720.
Conclusions: These data suggest that activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate-1 by FTY720 reduces neuronal death after transient MCAO.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Targeting the sphingolipid signaling pathway in stroke.Stroke. 2010 Apr;41(4):e193; author reply e194. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.578278. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Stroke. 2010. PMID: 20185772 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Role of the sphingosine metabolism pathway on neurons against experimental cerebral ischemia in rats.Transl Stroke Res. 2013 Oct;4(5):524-32. doi: 10.1007/s12975-013-0260-7. Transl Stroke Res. 2013. PMID: 24187597 Free PMC article.
-
Fingolimod provides long-term protection in rodent models of cerebral ischemia.Ann Neurol. 2011 Jan;69(1):119-29. doi: 10.1002/ana.22186. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Ann Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21280082 Free PMC article.
-
FTY720 ameliorates acute ischemic stroke in mice by reducing thrombo-inflammation but not by direct neuroprotection.Stroke. 2013 Nov;44(11):3202-10. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.002880. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 24029635
-
Phosphorylation of the immunomodulator FTY720 inhibits programmed cell death of fibroblasts via the S1P3 receptor subtype and Bcl-2 activation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(1):67-78. doi: 10.1159/000315107. Epub 2010 May 18. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20502006 Review.
-
The emerging role of FTY720 as a sphingosine 1-phosphate analog for the treatment of ischemic stroke: The cellular and molecular mechanisms.Brain Behav. 2021 Jun;11(6):e02179. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2179. Epub 2021 May 10. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33969931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fingolimod reduces hemorrhagic transformation associated with delayed tissue plasminogen activator treatment in a mouse thromboembolic model.Stroke. 2013 Feb;44(2):505-11. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.679043. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23287783 Free PMC article.
-
Fingolimod protects against neurovascular unit injury in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Apr;18(4):869-874. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.353500. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36204856 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors in Cerebral Ischemia.Neuromolecular Med. 2021 Mar;23(1):211-223. doi: 10.1007/s12017-020-08614-2. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Neuromolecular Med. 2021. PMID: 32914259 Review.
-
Sphingolipids in spinal cord injury.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 5;8(2):52-69. eCollection 2016. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27570580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Alzheimer's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Aug;56(8):5436-5455. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1448-3. Epub 2019 Jan 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30612333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singh IN, Hall ED. Multifaceted roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate: how does this bioactive sphingolipid fit with acute neurological injury? J Neurosci Res. 2008;86:1419–33. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Davis MD, Heise CE, Albert R, Cottens S, Hof R, Bruns C, Prieschl E, Baumruker T, Hiestand P, Foster CA, Zollinger M, Lynch KR. The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:21453–7. - PubMed
-
- Yagi H, Kamba R, Chiba K, Soga H, Yaguchi K, Nakamura M, Itoh T. Immunosuppressant FTY720 inhibits thymocyte emigration. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:1435–44. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Pinschewer DD, Feng L, Chen S. FTY720: altered lymphocyte traffic results in allograft protection. Transplantation. 2001;72:764–9. - PubMed
-
- Jung CG, Kim HJ, Miron VE, Cook S, Kennedy TE, Foster CA, Antel JP, Soliven B. Functional consequences of S1P receptor modulation in rat oligodendroglial lineage cells. Glia. 2007;55:1656–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

