Laminin gamma2 fragments are increased in the circulation of patients with early phase acute lung injury
- PMID: 19940975
- PMCID: PMC2820224
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-009-1719-6
Laminin gamma2 fragments are increased in the circulation of patients with early phase acute lung injury
Abstract
Objective: Laminin-5, a cell adhesive molecule expressed solely by epithelium, is known to enhance epithelial cell migration and repair of injured epithelium, after its essential component gamma2-chain is processed proteolytically. Our previous study revealed circulating levels of amino-terminal fragment of laminin gamma2-chain (G2F) reflect epithelial tumor invasiveness in carcinoma patients, but its physiological role in alveolar epithelial injury remains unknown.
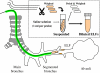
Design: Sampling of epithelial lining fluids or pulmonary edema fluids from patients with acute lung injury (ALI) or related diseases was performed. Plasma samples were obtained from them at the time of disease onset or later. G2F concentrations were determined by immunoassay constructed by ourselves.
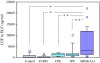
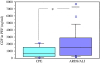
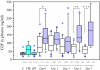
Results: We found a significantly higher amount of G2F in pulmonary edema and epithelial lining fluids of patients with ALI, as compared with those with the other respiratory diseases. Their plasma levels were also elevated significantly early at the onset of ALI (mean +/- SD; 147 +/- 82 ng/ml in non-surviving and 90 +/- 56 in surviving patients) as compared with those in the patients with cardiogenic pulmonary edema (59 +/- 36) or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (37 +/- 17), indicating alveolar epithelium rapidly secrete laminin-5 in ALI. At 5 days after onset, non-surviving patients maintained higher plasma concentrations (152 +/- 84), but in contrast, the levels in surviving patients declined (71 +/- 35), suggesting secretion of laminin-5 was suppressed, associated with recovery from ALI.
Conclusion: Circulating G2F may be a biomarker for alveolar laminin-5 secreted early at disease onset in ALI, potentially regulating alveolar re-epithelialization.
Figures
References
-
- Matthay MA, Wiener-Kronish JP. Intact epithelial barrier function is critical for the resolution for alveolar edema in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142:1250–1257. - PubMed
-
- Geiser T. Mechanisms of alveolar epithelial repair in acute lung injury—a translational approach. Swiss Med Wkly. 2003;133:586–590. - PubMed
-
- Adamson IYR, Bowden DH. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974;30:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Zahm JM, Chevillard M, Puchelle E. Wound repair of human surface respiratory epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991;5:242–248. - PubMed

