Pilocarpine-induced seizures produce alterations on choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities and deficit memory in rats
- PMID: 19941057
- PMCID: PMC11498744
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9481-4
Pilocarpine-induced seizures produce alterations on choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities and deficit memory in rats
Abstract
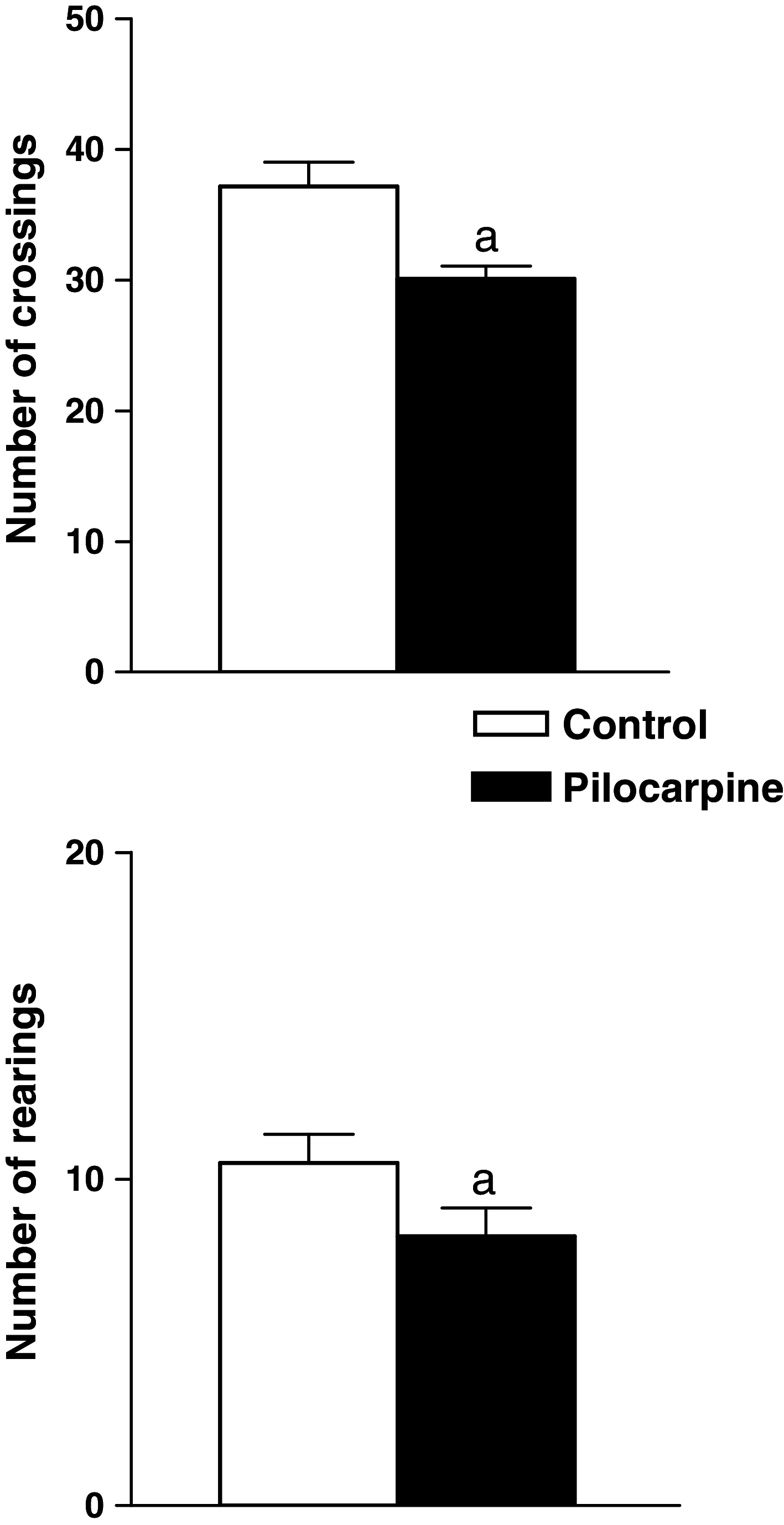
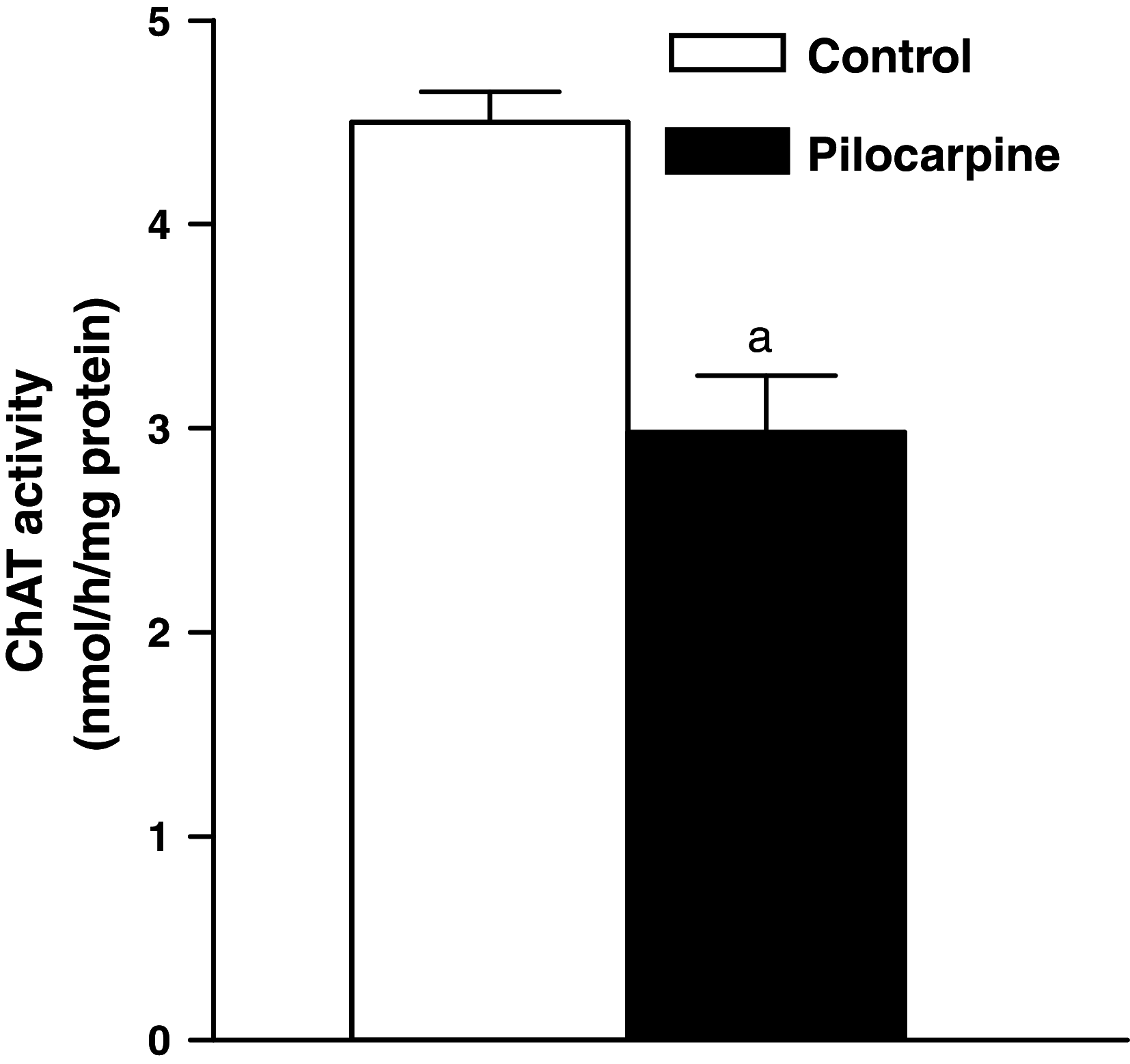
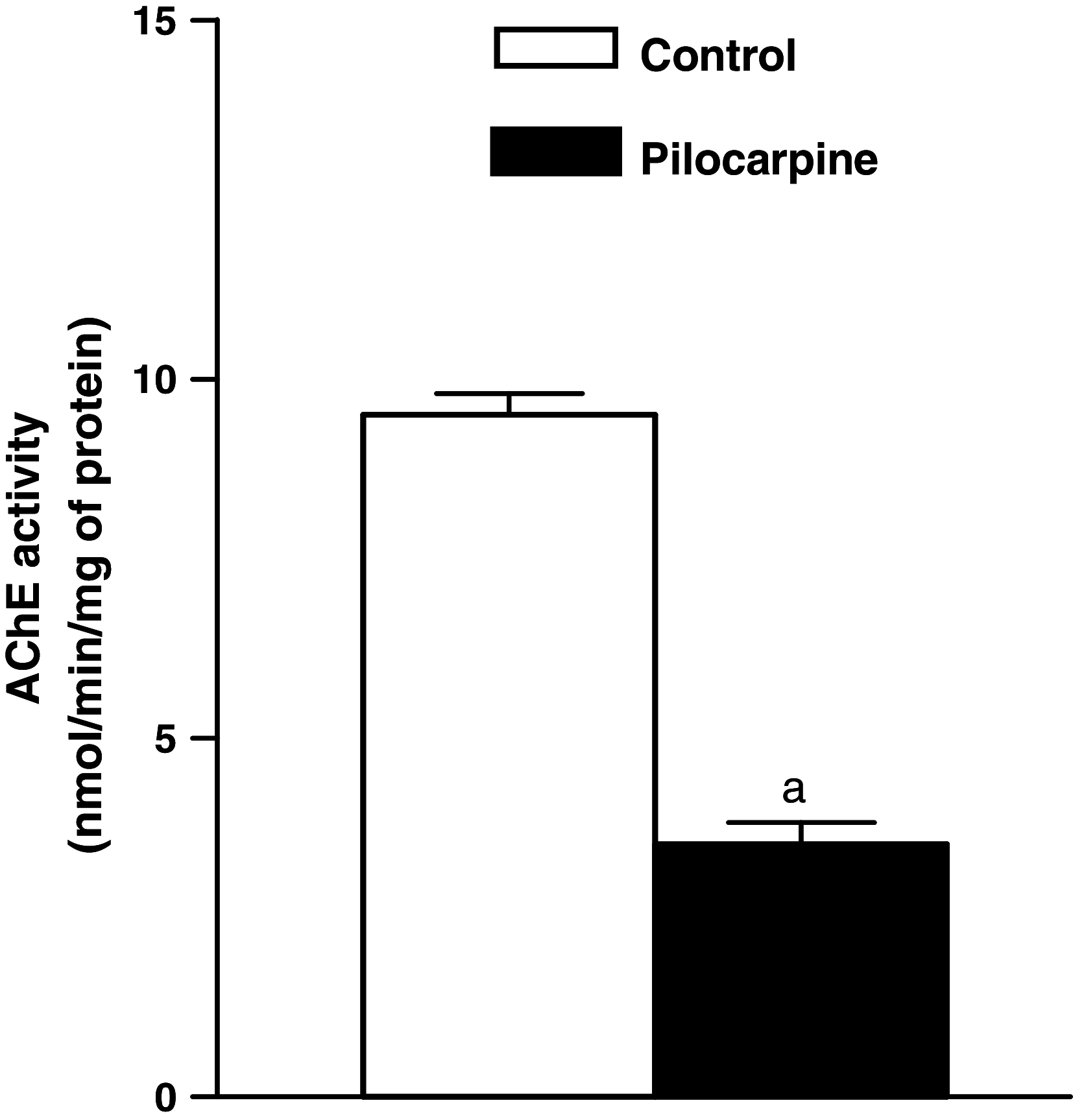
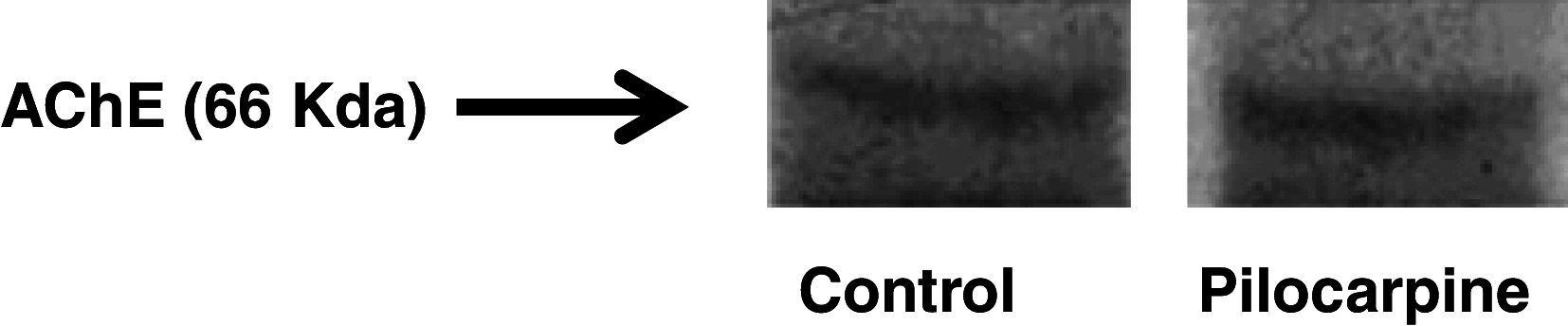
In the present study, we investigated the effect of seizures on rat performance in the Morris water maze task, as well as on choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activities in rat hippocampus. Wistar rats were treated with 0.9% saline (i.p., control group) and pilocarpine (400 mg/kg, i.p., pilocarpine group). After the treatments all groups were observed for 1 h. The changes on reference and working spatial memory caused by pilocarpine administration were observed in seized rats. The ChAT and AChE activities were measured using spectrophotometric methods and the results compared to values obtained from saline animals. Its activities were also determined after behavioral task. Results showed that seizures alter reference memory when compared to saline-treated animals. In the working memory task, we observed a significant day's effect with significant differences between control and pilocarpine-induced seizures. In pilocarpine group, it was observed a significant decreased in ChAT and AChE activities, when compared to control group. Our findings suggest that seizures caused cognitive dysfunction and a decrease of ChAT and AChE activities that might be related, at least in part, to the neurological problems presented by seizures induced by pilocarpine.
Figures
References
-
- Augoustides-Savvopoulou P, Luka Z, Karyda S, Karyda S, Stabler SP, Allen RH, Patsiaoura K, Wagner C, Mudd SH (2003) Glycine N-methyltransferase deficiency: a new patient with a novel mutation. J Inherit Metab Dis 26:745–759 - PubMed
-
- Cavalheiro EA, Leite JP, Bortolotto ZA, Turski WA, Ikonomidou C, Turski L (1991) Long-term effects of pilocarpine in rats: structural damage of the brain triggers kindling and spontaneous recurrent seizures. Epilepsia 32:778–782 - PubMed
-
- D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 36:60–90 - PubMed
-
- Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Sotne RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95 - PubMed
-
- Enz A, Amstutz R, Boddeke H, Gmelin G, Malanowski J (1993) Brain selective inhibition of acetylcholinesterase: a novel approach to therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Brain Res 98:431–438 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

