Fenretinide induces mitochondrial ROS and inhibits the mitochondrial respiratory chain in neuroblastoma
- PMID: 19941060
- PMCID: PMC2824117
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0212-2
Fenretinide induces mitochondrial ROS and inhibits the mitochondrial respiratory chain in neuroblastoma
Abstract
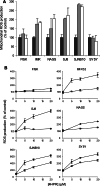
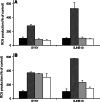
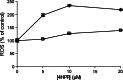
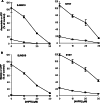
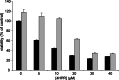
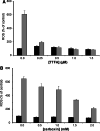
Fenretinide induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma by induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In this study, we investigated the role of mitochondria in fenretinide-induced cytotoxicity and ROS production in six neuroblastoma cell lines. ROS induction by fenretinide was of mitochondrial origin, demonstrated by detection of superoxide with MitoSOX, the scavenging effect of the mitochondrial antioxidant MitoQ and reduced ROS production in cells without a functional mitochondrial respiratory chain (Rho zero cells). In digitonin-permeabilized cells, a fenretinide concentration-dependent decrease in ATP synthesis and substrate oxidation was observed, reflecting inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. However, inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain was not required for ROS production. Co-incubation of fenretinide with inhibitors of different complexes of the respiratory chain suggested that fenretinide-induced ROS production occurred via complex II. The cytotoxicity of fenretinide was exerted through the generation of mitochondrial ROS and, at higher concentrations, also through inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GADD153 and 12-lipoxygenase mediate fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma.Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 15;62(18):5158-67. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12234979
-
Implication of mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species, cytochrome C and caspase-3 in N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in cervical carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 4;18(46):6380-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203024. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10597238
-
Mechanisms of free-radical induction in relation to fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Jul 1;89(4):698-708. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10551. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12858336
-
Molecular mechanisms of fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1028:81-9. doi: 10.1196/annals.1322.009. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15650234 Review.
-
Induction of GADD153 and Bak: novel molecular targets of fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2003 Jul 18;197(1-2):157-63. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00098-3. Cancer Lett. 2003. PMID: 12880976 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of fenretinide and selenite inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Nov 4;14(11):21790-804. doi: 10.3390/ijms141121790. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24192821 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic management of high-risk neuroblastoma in children.Paediatr Drugs. 2011 Aug 1;13(4):245-55. doi: 10.2165/11591630-000000000-00000. Paediatr Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21692548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for human mitochondrial complex II in the production of reactive oxygen species in human skin.Redox Biol. 2014;2:1016-22. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.08.005. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 25460738 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial supercomplex assembly regulates metabolic features and glutamine dependency in mammalian cells.Theranostics. 2023 May 21;13(10):3165-3187. doi: 10.7150/thno.78292. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37351168 Free PMC article.
-
Immune cells in the tumour: new routes of retinoids for chemoprevention and chemotherapeutics.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;175(23):4285-4294. doi: 10.1111/bph.14511. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30298911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Delia D, Aiello A, Lombardi L, Pelicci PG, Grignani F, Grignani F, Formelli F, Menard S, Costa A, Veronesi U. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide induces apoptosis of malignant hemopoietic cell lines including those unresponsive to retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 1993;53:6036–6041. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh TC, Ng C, Wu JM. The synthetic retinoid N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide (4-HPR) exerts antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing effects in the androgen-independent human prostatic JCA-1 cells. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1995;37:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrini R, Mariotti A, Tagliabue E, Bressan R, Bunone G, Coradini D, Della VG, Formelli F, Cleris L, Radice P. Modulation of markers associated with tumor aggressiveness in human breast cancer cell lines by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:863–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

