Progression through the RNA polymerase II CTD cycle
- PMID: 19941815
- PMCID: PMC3232742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.10.019
Progression through the RNA polymerase II CTD cycle
Abstract
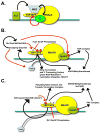
The C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II's largest subunit undergoes dynamic phosphorylation during transcription, and the different phosphorylation patterns that predominate at each stage of transcription recruit the appropriate set of mRNA-processing and histone-modifying factors. Recent papers help to explain how the changes in CTD phosphorylation pattern are linked to the progression from initiation through elongation to termination.
Figures
References
-
- Carninci P. Molecular biology: The long and short of RNAs. Nature. 2009;457:974–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

