alpha5 Subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors mediate a slowly decaying inhibitory synaptic current in CA1 pyramidal neurons following Schaffer collateral activation
- PMID: 19941877
- PMCID: PMC2814005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.11.005
alpha5 Subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors mediate a slowly decaying inhibitory synaptic current in CA1 pyramidal neurons following Schaffer collateral activation
Abstract
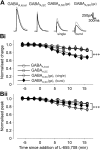
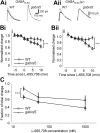
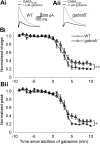
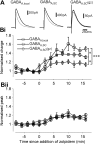
GABA(A) receptors that contain the alpha5 subunit (alpha5GABA(A)Rs) are highly expressed in the hippocampus, and have been implicated in learning and memory processes. They generate a tonic form of inhibition that regulates neuronal excitability. Recently it was shown that alpha5GABA(A)Rs also contribute to slow phasic inhibition of CA1 pyramidal neurons following local stimulation in the stratum lacunosum moleculare. However, it is unknown whether alpha5GABA(A)Rs can also be recruited indirectly by stimulation of Schaffer collaterals. Here, we studied GABAergic currents evoked by stimulation in the stratum radiatum of CA1 in the presence and absence of CNQX to block AMPA receptor-mediated excitation. We tested their sensitivity to gabazine and two drugs acting at the benzodiazepine site of alpha1/alpha2/alpha3 or alpha5GABA(A)Rs (400 nM zolpidem and 20 nM L-655,708, respectively). IPSCs evoked by stimulation in the stratum radiatum in the presence of CNQX were potentiated by zolpidem, blocked by 1 muM gabazine and were relatively insensitive to L-655,708 consistent with the lack of alpha5GABA(A)Rs. In contrast, IPSCs evoked by stimulation of Schaffer collaterals had a significant gabazine-insensitive component. This component was attenuated by L-655,708 and enhanced by burst stimulation. Furthermore, the L-655,708-sensitive current was absent in recordings from mice lacking alpha5GABA(A)Rs (gabra5(-/-) mice). These results show that alpha5GABA(A)R-mediated phasic inhibition is activated by the Schaffer collateral pathway and provide evidence for activity pattern-dependent participation of alpha5GABA(A)Rs in inhibition.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ali A.B., Thomson A.M. Synaptic α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors mediate IPSPs elicited by dendrite-preferring cells in rat neocortex. Cereb. Cortex. 2008;18:1260–1271. - PubMed
-
- Atack J.R., Bayley P.J., Seabrook G.R., Wafford K.A., McKernan R.M., Dawson G.R. L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for α5-containing GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51:1023–1029. - PubMed
-
- Ballard T.M., Knoflach F., Prinssen E., Borroni E., Vivian J.A., Basile J., Gasser R., Moreau J.L., Wettstein J.G., Buettelmann B., Knust H., Thomas A.W., Trube G., Hernandez M.C. RO4938581, a novel cognitive enhancer acting at GABAA α5 subunit-containing receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2009;202:207–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

