Exploring the mechanisms underlying surface-based stimulus selection
- PMID: 19941882
- PMCID: PMC2813929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.11.015
Exploring the mechanisms underlying surface-based stimulus selection
Abstract
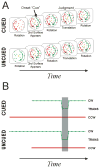
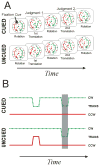
Valdes-Sosa, et al. (2000) introduced a transparent-motion design that provides evidence of surface-based processing of visual motion. We show that this design suffers from a motion-duration confound that admits an alternative explanation based on neuronal adaptation and competition. We tested this explanation by reversing the relationship between motion duration and which perceptual surface was "cued". We also examined the role of color duration. Our findings support the surface-based account and, more specifically, demonstrate that this type of surface-based selection involves selective spatial processing at the scale of the texture elements that define the transparent surfaces.
Figures



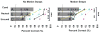


References
-
- Aine CJ, Harter MR. Visual event-related potentials to colored patterns and color names: attention to features and dimension. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986;64:228–45. - PubMed
-
- Andersen SK, Müller MM, Hillyard SA. Color-selective attention need not be mediated by spatial attention. J Vis. 8;9(6):2.1–7. - PubMed
-
- Anllo-Vento L, Hillyard SA. Selective attention to the color and direction of moving stimuli: electrophysiological correlates of hierarchical feature selection. Percept Psychophys. 1996;58:191–206. - PubMed
-
- Blaser E, Pylyshyn ZW, Holcombe AO. Tracking an object through feature space. Nature. 2000;9;408(6809):196–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

