HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism
- PMID: 19942427
- PMCID: PMC2822127
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.10.009
HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) plays a key role in the reprogramming of cancer metabolism by activating transcription of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic enzymes, which take up glucose and convert it to lactate; pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1, which shunts pyruvate away from the mitochondria; and BNIP3, which triggers selective mitochondrial autophagy. The shift from oxidative to glycolytic metabolism allows maintenance of redox homeostasis and cell survival under conditions of prolonged hypoxia. Many metabolic abnormalities in cancer cells increase HIF-1 activity. As a result, a feed-forward mechanism can be activated that drives HIF-1 activation and may promote tumor progression.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
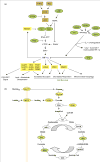
References
-
- Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:891–899. - PubMed
-
- Vaupel P, Mayer A, Hockel M. Tumor hypoxia and malignant progression. Methods Enzymol. 2004;381:335–354. - PubMed
-
- Mole DR, Blancher C, Copley RR, Pollard PJ, Gleadle JM, Ragoussis J, Ratcliffe PJ. Genome-wide association of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α DNA binding with expression profiling of hypoxia-inducible transcripts. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:16767–16775. The authors of this paper and ref. [4] performed ChIP-chip (chromatin immunoprecipitation and mRNA microarray) analysis to identify direct target genes of HIF-1 and HIF-2. The majority of hypoxia-induced genes contained HIF-1 binding sites and expression was dependent on HIF-1α expression. HIF-2α bound to many of the same genes, but knockdown of HIF-2α levels did not affect gene expression. Hypoxia-repressed gene expression was also HIF-1α-dependent but did not involve direct HIF-1α binding to target genes. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

