Deletion of ETS-1, a gene in the Jacobsen syndrome critical region, causes ventricular septal defects and abnormal ventricular morphology in mice
- PMID: 19942620
- PMCID: PMC2807373
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddp532
Deletion of ETS-1, a gene in the Jacobsen syndrome critical region, causes ventricular septal defects and abnormal ventricular morphology in mice
Abstract
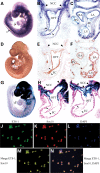
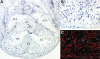
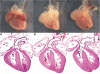
Congenital heart defects comprise the most common form of major birth defects, affecting 0.7% of all newborn infants. Jacobsen syndrome (11q-) is a rare chromosomal disorder caused by deletions in distal 11q. We have previously determined that a wide spectrum of the most common congenital heart defects occur in 11q-, including an unprecedented high frequency of hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS). We identified an approximately 7 Mb 'cardiac critical region' in distal 11q that contains a putative causative gene(s) for congenital heart disease. In this study, we utilized chromosomal microarray mapping to characterize three patients with 11q- and congenital heart defects that carry interstitial deletions overlapping the 7 Mb cardiac critical region. We propose that this 1.2 Mb region of overlap harbors a gene(s) that causes at least a subset of the congenital heart defects that occur in 11q-. We demonstrate that one gene in this region, ETS-1 (a member of the ETS family of transcription factors), is expressed in the endocardium and neural crest during early mouse heart development. Gene-targeted deletion of ETS-1 in mice in a C57/B6 background causes, with high penetrance, large membranous ventricular septal defects and a bifid cardiac apex, and less frequently a non-apex-forming left ventricle (one of the hallmarks of HLHS). Our results implicate an important role for the ETS-1 transcription factor in mammalian heart development and should provide important insights into some of the most common forms of congenital heart disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene-targeted deletion in mice of the Ets-1 transcription factor, a candidate gene in the Jacobsen syndrome kidney "critical region," causes abnormal kidney development.Am J Med Genet A. 2019 Jan;179(1):71-77. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.40481. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Am J Med Genet A. 2019. PMID: 30422383
-
Deletion of JAM-C, a candidate gene for heart defects in Jacobsen syndrome, results in a normal cardiac phenotype in mice.Am J Med Genet A. 2009 Jul;149A(7):1438-43. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32913. Am J Med Genet A. 2009. PMID: 19533782
-
Gene-targeted deletion of OPCML and Neurotrimin in mice does not yield congenital heart defects.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Apr;164A(4):966-74. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36441. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24616287
-
Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function.2016 Jun 25. In: Nakanishi T, Markwald RR, Baldwin HS, Keller BB, Srivastava D, Yamagishi H, editors. Etiology and Morphogenesis of Congenital Heart Disease: From Gene Function and Cellular Interaction to Morphology [Internet]. Tokyo: Springer; 2016. Chapter 52. 2016 Jun 25. In: Nakanishi T, Markwald RR, Baldwin HS, Keller BB, Srivastava D, Yamagishi H, editors. Etiology and Morphogenesis of Congenital Heart Disease: From Gene Function and Cellular Interaction to Morphology [Internet]. Tokyo: Springer; 2016. Chapter 52. PMID: 29787157 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Jacobsen syndrome: Advances in our knowledge of phenotype and genotype.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015 Sep;169(3):239-50. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31448. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26285164 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylation status of CpG sites in the NOTCH4 promoter region regulates NOTCH4 expression in patients with tetralogy of Fallot.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):4412-4422. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11535. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33000281 Free PMC article.
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell modelling of HLHS underlines the contribution of dysfunctional NOTCH signalling to impaired cardiogenesis.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Aug 15;26(16):3031-3045. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx140. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28521042 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Crest.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1441:125-143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44087-8_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38884708 Review.
-
Mutational screening of affected cardiac tissues and peripheral blood cells identified novel somatic mutations in GATA4 in patients with ventricular septal defect.J Biomed Res. 2011 Nov;25(6):425-30. doi: 10.1016/S1674-8301(11)60056-0. J Biomed Res. 2011. PMID: 23554720 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: current considerations and expectations.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Jan 3;59(1 Suppl):S1-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.09.022. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22192720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jacobsen P., Hauge M., Henningsen K., Hobolth N., Mikkelsen M., Philip J. An (11;21) translocation in four generations with chromosome 11 abnormalities in the offspring. Hum. Hered. 1973;2:568–585. - PubMed
-
- Grossfeld P.D., Mattina T., Lai Z., Favier R., Jones K.L., Cotter F., Jones C. The 11q terminal deletion disorder: a prospective study of 110 cases. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2004;15:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Oikawa T., Yamada T. Molecular biology of the Ets family of transcription factors. Gene. 2003;16:11–34. (Review) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

