Identification of natural pneumococcal isolates expressing serotype 6D by genetic, biochemical and serological characterization
- PMID: 19942663
- PMCID: PMC2890086
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.034116-0
Identification of natural pneumococcal isolates expressing serotype 6D by genetic, biochemical and serological characterization
Abstract
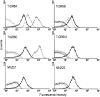
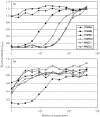
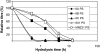
The recently discovered pneumococcal serotype 6C was created when the original wciN gene in the 6A capsule gene locus was naturally replaced with a new gene. Since the capsule gene loci of 6A and 6B serotypes may differ by only one base pair in the wciP gene, it was speculated that a new serotype '6D' would be possible if the new wciN gene were inserted into the 6B capsule gene locus. Although pneumococci expressing serotype 6D could be produced in the laboratory, initial searches for natural pneumococcal isolates expressing serotype 6D were unsuccessful. However, we now report the discovery of two naturally occurring pneumococcal isolates from Korea that have the serological, genetic and biochemical features predicted for serotype 6D.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of capsular genes of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6A, 6B, 6C, and 6D isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2011 May;49(5):1758-64. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02628-10. Epub 2011 Mar 16. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21411593 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic, biochemical, and serological characterization of a new pneumococcal serotype, 6H, and generation of a pneumococcal strain producing three different capsular repeat units.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Mar;22(3):313-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00647-14. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25589550 Free PMC article.
-
Production of a unique pneumococcal capsule serotype belonging to serogroup 6.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Feb;155(Pt 2):576-583. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.024521-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19202106 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the capsular gene locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 6.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jan;157(Pt 1):189-198. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.043901-0. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 20929956 Free PMC article.
-
Capsular polysaccharide gene diversity of pneumococcal serotypes 6A, 6B, 6C, and 6D.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Nov;304(8):1109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25220816
Cited by
-
Pneumococcal serotypes before and after introduction of conjugate vaccines, United States, 1999-2011(1.).Emerg Infect Dis. 2013 Jul;19(7):1074-83. doi: 10.3201/eid1907.121830. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23763847 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 6 isolates from IPD in children and adults in Germany.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 9;8(4):e60848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060848. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593324 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial capsules: Occurrence, mechanism, and function.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Mar 13;10(1):21. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00497-6. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 38480745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a fourfold multiplexed opsonophagocytosis assay for pneumococcal antibodies against additional serotypes and discovery of serological subtypes in Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 20.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Jun;19(6):835-41. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00086-12. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22518015 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6D clones in South Korea.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Mar;50(3):818-22. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05895-11. Epub 2011 Dec 14. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22170935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cole, R. (1913). Treatment of pneumonia by means of specific serums. JAMA 61, 663–666.
-
- Enright, M. C. & Spratt, B. G. (1998). A multilocus sequence typing scheme for Streptococcus pneumoniae: identification of clones associated with serious invasive disease. Microbiology 144, 3049–3060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

