Defining a role for Hfq in Gram-positive bacteria: evidence for Hfq-dependent antisense regulation in Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 19942685
- PMCID: PMC2817478
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1081
Defining a role for Hfq in Gram-positive bacteria: evidence for Hfq-dependent antisense regulation in Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
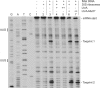
Small trans-encoded RNAs (sRNAs) modulate the translation and decay of mRNAs in bacteria. In Gram-negative species, antisense regulation by trans-encoded sRNAs relies on the Sm-like protein Hfq. In contrast to this, Hfq is dispensable for sRNA-mediated riboregulation in the Gram-positive species studied thus far. Here, we provide evidence for Hfq-dependent translational repression in the Gram-positive human pathogen Listeria monocytogenes, which is known to encode at least 50 sRNAs. We show that the Hfq-binding sRNA LhrA controls the translation and degradation of its target mRNA by an antisense mechanism, and that Hfq facilitates the binding of LhrA to its target. The work presented here provides the first experimental evidence for Hfq-dependent riboregulation in a Gram-positive bacterium. Our findings indicate that modulation of translation by trans-encoded sRNAs may occur by both Hfq-dependent and -independent mechanisms, thus adding another layer of complexity to sRNA-mediated riboregulation in Gram-positive species.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Translational regulation by bacterial small RNAs via an unusual Hfq-dependent mechanism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Mar 16;46(5):2585-2599. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1286. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29294046 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small Hfq-binding RNAs in Listeria monocytogenes.RNA. 2006 Jul;12(7):1383-96. doi: 10.1261/rna.49706. Epub 2006 May 8. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16682563 Free PMC article.
-
A small RNA controls expression of the chitinase ChiA in Listeria monocytogenes.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 18;6(4):e19019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019019. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21533114 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of the Hfq protein to translation regulation by small noncoding RNAs binding to the mRNA coding sequence.Acta Biochim Pol. 2016;63(4):701-707. doi: 10.18388/abp.2016_1362. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Acta Biochim Pol. 2016. PMID: 27878140 Review.
-
Identification and Role of Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in Listeria monocytogenes.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(8):5070-9. doi: 10.3390/ijms12085070. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21954346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of RNAs with Bacillus subtilis Hfq.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055156. Epub 2013 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457461 Free PMC article.
-
MouR controls the expression of the Listeria monocytogenes Agr system and mediates virulence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Oct 12;46(18):9338-9352. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky624. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30011022 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes Relies on the Heme-Regulated Transporter hrtAB to Resist Heme Toxicity and Uses Heme as a Signal to Induce Transcription of lmo1634, Encoding Listeria Adhesion Protein.Front Microbiol. 2018 Dec 18;9:3090. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03090. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30619169 Free PMC article.
-
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa PrrF1 and PrrF2 Small Regulatory RNAs Promote 2-Alkyl-4-Quinolone Production through Redundant Regulation of the antR mRNA.J Bacteriol. 2018 Apr 24;200(10):e00704-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00704-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29507088 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Adaptation to Antibiotics through Regulatory RNAs.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Apr 26;62(5):e02503-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02503-17. Print 2018 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29530859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cossart P, Toledo-Arana A. Listeria monocytogenes, a unique model in infection biology: an overview. Microbes Infect. 2008;10:1041–1050. - PubMed
-
- Toledo-Arana A, Dussurget O, Nikitas G, Sesto N, Guet-Revillet H, Balestrino D, Loh E, Gripenland J, Tiensuu T, Vaitkevicius K, et al. The Listeria transcriptional landscape from saprophytism to virulence. Nature. 2009;459:950–956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

