Role of MR imaging in prenatal diagnosis of pregnancies at risk for Joubert syndrome and related cerebellar disorders
- PMID: 19942698
- PMCID: PMC7963961
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1867
Role of MR imaging in prenatal diagnosis of pregnancies at risk for Joubert syndrome and related cerebellar disorders
Abstract
Background and purpose: JSRD are rare autosomal recessive brain malformations. We hypothesized that MR imaging can assess fetuses at risk for JSRD and might influence their diagnoses.
Materials and methods: We prospectively performed cranial MR imaging for 12 fetuses (mean GA, 23 weeks; SD, 3.7) at 25% recurrence risk for JSRD. We correlated prenatal MR imaging findings with postnatal MR imaging and clinical outcome. Retrospectively, we compared posterior fossa measurements of the cases with those of 24 age-matched fetuses with proved normal brain MR imaging. Institutional review board approval and consents were obtained. Statistical methods included a t test and ANCOVA tests.
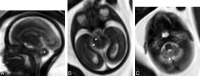
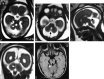
Results: Fetal MR imaging correctly diagnosed 3 cases at 22, 28, and 29 weeks of gestation as JSRD, and 9 cases as normal. In JSRD-affected fetuses, prenatal MR imaging detected narrow pontomesencephalic junction (isthmus) with deepening of the interpeduncular fossa and thick horizontally placed superior cerebellar peduncles (MTS), deformed anteriorly convex floor of the fourth ventricle, and midline cerebellar cleft in place of the hypoplastic vermis. Measurements on axial fetal MR imaging at pontomesencephalic junction, ratio of AP diameters of interpeduncular fossa to midbrain/isthmus, and ratio of the AP to transverse diameters of the fourth ventricle were significantly higher in JSRD-affected fetuses than in nonaffected cases and the control group.
Conclusions: MR imaging can diagnose JSRD in at-risk pregnancies by detecting posterior fossa signs. Measurements at the pontomesencephalic junction may enhance fetal MR imaging accuracy in diagnosing JSRD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Joubert syndrome and related disorders, prenatal diagnosis with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2012 Jun 1;13(2):135-8. doi: 10.5152/jtgga.2011.75. eCollection 2012. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2012. PMID: 24592023 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal abnormal features of the fourth ventricle in Joubert syndrome and related disorders.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Feb;43(2):227-32. doi: 10.1002/uog.12567. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 23868831
-
Multidimensional analysis of fetal posterior fossa in health and disease.Cerebellum. 2013 Oct;12(5):632-44. doi: 10.1007/s12311-013-0470-2. Cerebellum. 2013. PMID: 23553467
-
Posterior fossa malformations.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2011 Jun;32(3):228-41. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2011.02.003. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2011. PMID: 21596278 Review.
-
Pre- and Postnatal Neuroimaging of Congenital Cerebellar Abnormalities.Cerebellum. 2016 Feb;15(1):5-9. doi: 10.1007/s12311-015-0699-z. Cerebellum. 2016. PMID: 26166429 Review.
Cited by
-
Healthcare recommendations for Joubert syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Jan;182(1):229-249. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61399. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 31710777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ciliopathies in neuronal development: a clinical approach to investigation of Joubert syndrome and Joubert syndrome-related disorders.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011 Sep;53(9):793-798. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.04021.x. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21679365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joubert syndrome: congenital cerebellar ataxia with the molar tooth.Lancet Neurol. 2013 Sep;12(9):894-905. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70136-4. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Lancet Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23870701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Midbrain and hindbrain malformations: advances in clinical diagnosis, imaging, and genetics.Lancet Neurol. 2013 Apr;12(4):381-93. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70024-3. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Lancet Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23518331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joubert syndrome in a neonate: case report with literature review.Sudan J Paediatr. 2016;16(1):53-7. Sudan J Paediatr. 2016. PMID: 27651554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joubert M, Eisenring JJ, Andermann F. Familial dysgenesis of the vermis: a syndrome of hyperventilation, abnormal eye movements and retardation. Neurology 1968;18:302–03 - PubMed
-
- Maria BL, Boltshauser E, Palmer SC, et al. . Clinical features and revised diagnostic criteria in Joubert syndrome. J Child Neurol 1999;14:583–50 - PubMed
-
- Chance PF, Cavalier L, Satran D, et al. . Clinical nosologic and genetic aspects of Joubert and related syndromes. J Child Neurol 1999;14:660–66 - PubMed
-
- Valente EM, Marsh SE, Castori M, et al. . Distinguishing the four genetic causes of Joubert syndrome-related disorders. Ann Neurol 2005;57:513–19 - PubMed
-
- Maria BL, Quisling RG, Rosainz LC, et al. . Molar tooth sign in Joubert syndrome: clinical, radiological, and pathological significance. J Child Neurol 1999;14:368–76 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
