Structural insights into the dual nucleotide exchange and GDI displacement activity of SidM/DrrA
- PMID: 19942850
- PMCID: PMC2824451
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.347
Structural insights into the dual nucleotide exchange and GDI displacement activity of SidM/DrrA
Abstract
GDP-bound prenylated Rabs, sequestered by GDI (GDP dissociation inhibitor) in the cytosol, are delivered to destined sub-cellular compartment and subsequently activated by GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factors) catalysing GDP-to-GTP exchange. The dissociation of GDI from Rabs is believed to require a GDF (GDI displacement factor). Only two RabGDFs, human PRA-1 and Legionella pneumophila SidM/DrrA, have been identified so far and the molecular mechanism of GDF is elusive. Here, we present the structure of a SidM/DrrA fragment possessing dual GEF and GDF activity in complex with Rab1. SidM/DrrA reconfigures the Switch regions of the GTPase domain of Rab1, as eukaryotic GEFs do toward cognate Rabs. Structure-based mutational analyses show that the surface of SidM/DrrA, catalysing nucleotide exchange, is involved in GDI1 displacement from prenylated Rab1:GDP. In comparison with an eukaryotic GEF TRAPP I, this bacterial GEF/GDF exhibits high binding affinity for Rab1 with GDP retained at the active site, which appears as the key feature for the GDF activity of the protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


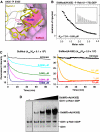
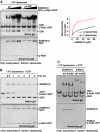


Similar articles
-
RabGDI displacement by DrrA from Legionella is a consequence of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity.Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 25;36(6):1060-72. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.014. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 20064470
-
Structural insights into a unique Legionella pneumophila effector LidA recognizing both GDP and GTP bound Rab1 in their active state.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(3):e1002528. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002528. Epub 2012 Mar 1. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22416225 Free PMC article.
-
A bifunctional bacterial protein links GDI displacement to Rab1 activation.Science. 2007 Nov 9;318(5852):974-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1149121. Epub 2007 Oct 18. Science. 2007. PMID: 17947549
-
De-AMPylation unmasked: modulation of host membrane trafficking.Sci Signal. 2011 Oct 11;4(194):pe42. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002458. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21990428 Review.
-
Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jan;93(1):269-309. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00003.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23303910 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural mechanism of host Rab1 activation by the bifunctional Legionella type IV effector SidM/DrrA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 9;107(10):4699-704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914231107. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20176951 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology.Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):119-49. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00059.2009. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21248164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jul;93(3):1019-137. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00028.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23899561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural analyses of Legionella LepB reveal a new GAP fold that catalytically mimics eukaryotic RasGAP.Cell Res. 2013 Jun;23(6):775-87. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.54. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23588383 Free PMC article.
-
Rabs on the fly: Functions of Rab GTPases during development.Small GTPases. 2019 Mar;10(2):89-98. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1279725. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28118081 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali BR, Seabra MC (2005) Targeting of Rab GTPases to cellular membranes. Biochem Soc Trans 33(Part 4): 652–656 - PubMed
-
- Allan BB, Moyer BD, Balch WE (2000) Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 289: 444–448 - PubMed
-
- Araki S, Kikuchi A, Hata Y, Isomura M, Takai Y (1990) Regulation of reversible binding of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, to synaptic plasma membranes and vesicles by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Biol Chem 265: 13007–13015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

