Analysis of small RNA in fission yeast; centromeric siRNAs are potentially generated through a structured RNA
- PMID: 19942857
- PMCID: PMC2797062
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.351
Analysis of small RNA in fission yeast; centromeric siRNAs are potentially generated through a structured RNA
Abstract
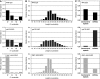
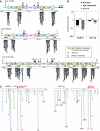
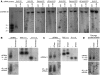
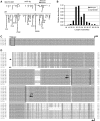
The formation of heterochromatin at the centromeres in fission yeast depends on transcription of the outer repeats. These transcripts are processed into siRNAs that target homologous loci for heterochromatin formation. Here, high throughput sequencing of small RNA provides a comprehensive analysis of centromere-derived small RNAs. We found that the centromeric small RNAs are Dcr1 dependent, carry 5'-monophosphates and are associated with Ago1. The majority of centromeric small RNAs originate from two remarkably well-conserved sequences that are present in all centromeres. The high degree of similarity suggests that this non-coding sequence in itself may be of importance. Consistent with this, secondary structure-probing experiments indicate that this centromeric RNA is partially double-stranded and is processed by Dicer in vitro. We further demonstrate the existence of small centromeric RNA in rdp1Delta cells. Our data suggest a pathway for siRNA generation that is distinct from the well-documented model involving RITS/RDRC. We propose that primary transcripts fold into hairpin-like structures that may be processed by Dcr1 into siRNAs, and that these siRNAs may initiate heterochromatin formation independent of RDRC activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Allshire RC, Nimmo ER, Ekwall K, Javerzat JP, Cranston G (1995) Mutations derepressing silent centromeric domains in fission yeast disrupt chromosome segregation. Genes Dev 9: 218–233 - PubMed
-
- Appelgren H, Kniola B, Ekwall K (2003) Distinct centromere domain structures with separate functions demonstrated in live fission yeast cells. J Cell Sci 116 (Pt 19): 4035–4042 - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124 - PubMed
-
- Bernard P, Maure JF, Partridge JF, Genier S, Javerzat JP, Allshire RC (2001) Requirement of heterochromatin for cohesion at centromeres. Science 294: 2539–2542 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

