Adverse stress, hippocampal networks, and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19943124
- PMCID: PMC2833224
- DOI: 10.1007/s12017-009-8107-9
Adverse stress, hippocampal networks, and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
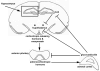
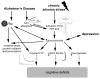
Recent clinical data have implicated chronic adverse stress as a potential risk factor in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and data also suggest that normal, physiological stress responses may be impaired in AD. It is possible that pathology associated with AD causes aberrant responses to chronic stress, due to potential alterations in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Recent study in rodent models of AD suggests that chronic adverse stress exacerbates the cognitive deficits and hippocampal pathology that are present in the AD brain. This review summarizes recent findings obtained in experimental AD models regarding the influence of chronic adverse stress on the underlying cellular and molecular disease processes including the potential role of glucocorticoids. Emerging findings suggest that both AD and chronic adverse stress affect hippocampal neural networks in a similar fashion. We describe alterations in hippocampal plasticity, which occur in both chronic stress and AD including dendritic remodeling, neurogenesis, and long-term potentiation. Finally, we outline potential roles for oxidative stress and neurotrophic factor signaling as the key determinants of the impact of chronic stress on the plasticity of neural networks and AD pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Aisa B, Elizalde N, Tordera R, Lasheras B, Del Río J, Ramírez MJ. Effects of neonatal stress on markers of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: Implications for spatial memory. Hippocampus. 2009 epub. - PubMed
-
- Aleisa AM, Alzoubi KH, Gerges NZ, Alkadhi KA. Chronic psychosocial stress-induced impairment of hippocampal LTP: possible role of BDNF. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;22:453–462. - PubMed
-
- Alfarez DN, Joëls M, Krugers HJ. Chronic unpredictable stress impairs long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal CA1 area and dentate gyrus in vitro. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:1928–1934. - PubMed
-
- Alfarez DN, Weigert O, Joëls M, Krugers HJ. Corticosterone and stress reduce synaptic potentiation in mouse hippocampal slices with mild stimulation. Neurosci. 2002;115:1119–1126. - PubMed
-
- Atif F, Yousuf S, Agrawal SK. Restraint stress-induced oxidative damage and its amelioration with selenium. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;600:59–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

