Hypercholesterolemia and myocardial function evaluated via tissue doppler imaging
- PMID: 19943937
- PMCID: PMC2794260
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-7-56
Hypercholesterolemia and myocardial function evaluated via tissue doppler imaging
Abstract
Objective: To establish a link between hypercholesterolemia and myocardial dysfunction.
Background: Heart failure is a complex disease involving changes in systolic and diastolic function. Newer echocardiographic imaging modalities may be able to detect discreet changes in myocardial function associated with hypercholesterolemia. Therefore we sought to establish a link between hypercholesterolemia and myocardial dysfunction with tissue Doppler imaging (TDI).
Methods: Twenty-seven rabbits were studied: 7 were fed normal chow (group 1) and 20 a high cholesterol diet (10 with ezetimibe, 1 mg/kg/day; group 2 and 10 without, group 3). Echocardiographic images were obtained under general anesthesia. Serum cholesterol levels were obtained at baseline, 3 and 6 months and myocardial cholesterol levels measured following euthanasia.
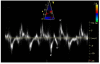
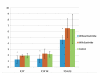
Results: Doppler measurements, including E/A, E'/A' and S' were significantly lower in group 3 compared to both groups 1 and 2 but no significant differences were noted in chamber sizes or ejection fraction among the groups. Average serum cholesterol was higher in group 3 compared to groups 1 and 2 respectively (495 +/- 305 mg/dl vs. 114 +/- 95 mg/dl and 87 +/- 37 mg/dl; p < 0.01). Myocardial cholesterol content was also higher in group 3 compared to group 2 (0.10 +/- 0.04 vs. 0.06 mg/dl +/- 0.02; p = 0.05). There was significant correlation between S', E'/A', E/E' and serum cholesterol (r2 = 0.17 p = 0.04, r2 = 0.37 p = 0.001 and r2 = 0.24 p = 0.01).
Conclusion: Cholesterol load in the serum and myocardium was significantly associated with decreased systolic and diastolic function by TDI. Moreover, lipid lowering was protective.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impaired Systolic and Diastolic Left Ventricular Function in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease - Results from the 4C Study.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 7;9(1):11462. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46653-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31391470 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of maintenance recombinant human erythropoietin therapy on ambulatory blood pressure recordings: conventional, Doppler, and tissue Doppler echocardiographic parameters.Artif Organs. 2005 Dec;29(12):965-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2005.00166.x. Artif Organs. 2005. PMID: 16305652 Clinical Trial.
-
Usefulness of tissue Doppler imaging to predict arrhythmic events in adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot.Rev Port Cardiol. 2010 Jul-Aug;29(7-8):1145-61. Rev Port Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 21066968 English, Portuguese.
-
Tissue Doppler echocardiography reveals distinct patterns of impaired myocardial velocities in different degrees of coronary artery disease.Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010 Jul;11(6):544-9. doi: 10.1093/ejechocard/jeq015. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010. PMID: 20207722
-
RV contractility and exercise-induced pulmonary hypertension in chronic mountain sickness: a stress echocardiographic and tissue Doppler imaging study.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Dec;6(12):1287-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Oct 23. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 24269266
Cited by
-
Cholesterol lowering attenuates pressure overload-induced heart failure in mice with mild hypercholesterolemia.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Sep 4;11(17):6872-6891. doi: 10.18632/aging.102218. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31484164 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Leads to Cardiac Dysfunction and Alterations in the Myocardial Proteome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 2;23(13):7387. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137387. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806390 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac tissue Doppler and tissue velocity imaging in anesthetized New Zealand white rabbits.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2011 May;50(3):317-21. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2011. PMID: 21640025 Free PMC article.
-
The human phospholamban Arg14-deletion mutant localizes to plasma membrane and interacts with the Na/K-ATPase.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Mar;52(3):773-82. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.11.012. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22155237 Free PMC article.
-
Hypercholesterolemia affects cardiac function, infarct size and inflammation in APOE*3-Leiden mice following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 14;14(6):e0217582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217582. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31199833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O'Donnell CJ, Roger V, Rumsfeld J, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Hong Y. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115:e69–171. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.179918. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP, Anderson K, Wilson PW, Levy D. Lipids and risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Annals of Epidemiology. pp. 23–8. - PubMed
-
- Stokes KY, Cooper D, Tailor A, Granger DN. Hypercholesterolemia promotes inflammation and microvascular dysfunction: Role of nitric oxide and superoxide. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 2002;33:1026–1036. - PubMed
-
- Simes J, Furberg CD, Braunwald E, Davis BR, Ford I, Tonkin A, Shepherd J. Effects of pravastatin on mortality in patients with and without coronary heart disease across a broad range of cholesterol levels. The Prospective Pravastatin Pooling project. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:207–15. doi: 10.1053/euhj.2001.2775. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

