Hypercholesterolemia and myocardial function evaluated via tissue doppler imaging
- PMID: 19943937
- PMCID: PMC2794260
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-7-56
Hypercholesterolemia and myocardial function evaluated via tissue doppler imaging
Abstract
Objective: To establish a link between hypercholesterolemia and myocardial dysfunction.
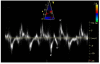
Background: Heart failure is a complex disease involving changes in systolic and diastolic function. Newer echocardiographic imaging modalities may be able to detect discreet changes in myocardial function associated with hypercholesterolemia. Therefore we sought to establish a link between hypercholesterolemia and myocardial dysfunction with tissue Doppler imaging (TDI).
Methods: Twenty-seven rabbits were studied: 7 were fed normal chow (group 1) and 20 a high cholesterol diet (10 with ezetimibe, 1 mg/kg/day; group 2 and 10 without, group 3). Echocardiographic images were obtained under general anesthesia. Serum cholesterol levels were obtained at baseline, 3 and 6 months and myocardial cholesterol levels measured following euthanasia.
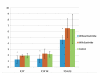
Results: Doppler measurements, including E/A, E'/A' and S' were significantly lower in group 3 compared to both groups 1 and 2 but no significant differences were noted in chamber sizes or ejection fraction among the groups. Average serum cholesterol was higher in group 3 compared to groups 1 and 2 respectively (495 +/- 305 mg/dl vs. 114 +/- 95 mg/dl and 87 +/- 37 mg/dl; p < 0.01). Myocardial cholesterol content was also higher in group 3 compared to group 2 (0.10 +/- 0.04 vs. 0.06 mg/dl +/- 0.02; p = 0.05). There was significant correlation between S', E'/A', E/E' and serum cholesterol (r2 = 0.17 p = 0.04, r2 = 0.37 p = 0.001 and r2 = 0.24 p = 0.01).
Conclusion: Cholesterol load in the serum and myocardium was significantly associated with decreased systolic and diastolic function by TDI. Moreover, lipid lowering was protective.
Figures

References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O'Donnell CJ, Roger V, Rumsfeld J, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Hong Y. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115:e69–171. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.179918. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP, Anderson K, Wilson PW, Levy D. Lipids and risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Annals of Epidemiology. pp. 23–8. - PubMed
-
- Stokes KY, Cooper D, Tailor A, Granger DN. Hypercholesterolemia promotes inflammation and microvascular dysfunction: Role of nitric oxide and superoxide. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 2002;33:1026–1036. - PubMed
-
- Simes J, Furberg CD, Braunwald E, Davis BR, Ford I, Tonkin A, Shepherd J. Effects of pravastatin on mortality in patients with and without coronary heart disease across a broad range of cholesterol levels. The Prospective Pravastatin Pooling project. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:207–15. doi: 10.1053/euhj.2001.2775. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

