Salt-dependent regulation of a CNG channel subfamily in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 19943938
- PMCID: PMC2794285
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-140
Salt-dependent regulation of a CNG channel subfamily in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Background: In Arabidopsis thaliana, the family of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (CNGCs) is composed of 20 members. Previous studies indicate that plant CNGCs are involved in the control of growth processes and responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. According to their proposed function as cation entry pathways these channels contribute to cellular cation homeostasis, including calcium and sodium, as well as to stress-related signal transduction. Here, we studied the expression patterns and regulation of CNGC19 and CNGC20, which constitute one of the five CNGC subfamilies.
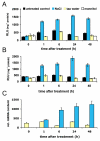
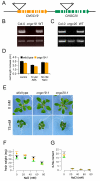
Results: GUS, GFP and luciferase reporter assays were used to study the expression of CNGC19 and CNGC20 genes from Arabidopsis thaliana in response to developmental cues and salt stress. CNGC19 and CNGC20 were differentially expressed in roots and shoots. The CNGC19 gene was predominantly active in roots already at early growth stages. Major expression was observed in the phloem. CNGC20 showed highest promoter activity in mesophyll cells surrounding the veins. Its expression increased during development and was maximal in mature and senescent leaves. Both genes were upregulated in the shoot in response to elevated NaCl but not mannitol concentrations. While in the root, CNGC19 did not respond to changes in the salt concentration, in the shoot it was strongly upregulated in the observed time frame (6-72 hours). Salt-induction of CNGC20 was also observed in the shoot, starting already one hour after stress treatment. It occurred with similar kinetics, irrespective of whether NaCl was applied to roots of intact plants or to the petiole of detached leaves. No differences in K and Na contents of the shoots were measured in homozygous T-DNA insertion lines for CNGC19 and CNGC20, respectively, which developed a growth phenotype in the presence of up to 75 mM NaCl similar to that of the wild type.
Conclusion: Together, the results strongly suggest that both channels are involved in the salinity response of different cell types in the shoot. Upon salinity both genes are upregulated within hours. CNGC19 and CNGC20 could assist the plant to cope with toxic effects caused by salt stress, probably by contributing to a re-allocation of sodium within the plant.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A mis-regulated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mediates cytosolic calcium elevation and activates immunity in Arabidopsis.New Phytol. 2021 May;230(3):1078-1094. doi: 10.1111/nph.17218. Epub 2021 Feb 26. New Phytol. 2021. PMID: 33469907
-
The Receptor Kinases BAK1/SERK4 Regulate Ca2+ Channel-Mediated Cellular Homeostasis for Cell Death Containment.Curr Biol. 2019 Nov 18;29(22):3778-3790.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.09.018. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31679931 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic nucleotide gated channel 10 negatively regulates salt tolerance by mediating Na+ transport in Arabidopsis.J Plant Res. 2015 Jan;128(1):211-20. doi: 10.1007/s10265-014-0679-2. Epub 2014 Nov 23. J Plant Res. 2015. PMID: 25416933
-
The role of shoot-derived RNAs transported to plant root in response to abiotic stresses.Plant Sci. 2023 Mar;328:111570. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111570. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36563939 Review.
-
Shoot-Root Communication in Flowering Plants.Curr Biol. 2017 Sep 11;27(17):R973-R978. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.06.054. Curr Biol. 2017. PMID: 28898670 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Experimental Expression Analysis of CNGC Gene Family in Gossypium.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 27;24(5):4617. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054617. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902047 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic AMP: A Polyhedral Signalling Molecule in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 9;21(14):4862. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144862. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32660128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consequences of SOS1 deficiency: intracellular physiology and transcription.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Jun;5(6):766-8. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp391.. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20505347 Free PMC article.
-
Piriformospora indica confers salinity tolerance on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) through amelioration of nutrient accumulation, K+/Na+ homeostasis and water status.Plant Cell Rep. 2019 Sep;38(9):1151-1163. doi: 10.1007/s00299-019-02434-w. Epub 2019 May 31. Plant Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31152194
-
Deciphering the Role of Ion Channels in Early Defense Signaling against Herbivorous Insects.Cells. 2021 Aug 27;10(9):2219. doi: 10.3390/cells10092219. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

