Non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src is required for ischemia-stimulated neuronal cell proliferation via Raf/ERK/CREB activation in the dentate gyrus
- PMID: 19943942
- PMCID: PMC2794287
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-139
Non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src is required for ischemia-stimulated neuronal cell proliferation via Raf/ERK/CREB activation in the dentate gyrus
Abstract
Background: Neurogenesis in the adult mammalian hippocampus may contribute to repairing the brain after injury. However, Molecular mechanisms that regulate neuronal cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus (DG) following ischemic stroke insult are poorly understood. This study was designed to investigate the potential regulatory capacity of non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src on ischemia-stimulated cell proliferation in the adult DG and its underlying mechanism.
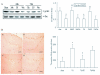
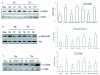
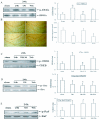
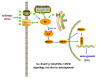
Results: Src kinase activated continuously in the DG 24 h and 72 h after transient global ischemia, while SU6656, the Src kinase inhibitor significantly decreased the number of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) labeling-positive cells of rats 7 days after cerebral ischemia in the DG, as well as down-regulated Raf phosphorylation at Tyr(340/341) site, and its down-stream signaling molecules ERK and CREB expression followed by 24 h and 72 h of reperfusion, suggesting a role of Src kinase as an enhancer on neuronal cell proliferation in the DG via modifying the Raf/ERK/CREB cascade. This hypothesis is supported by further findings that U0126, the ERK inhibitor, induced a reduction of adult hippocampal progenitor cells in DG after cerebral ischemia and down-regulated phospho-ERK and phospho-CREB expression, but no effect was detected on the activities of Src and Raf.
Conclusion: Src kinase increase numbers of newborn neuronal cells in the DG via the activation of Raf/ERK/CREB signaling cascade after cerebral ischemia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sustained activation of Src-family tyrosine kinases by ischemia: a potential mechanism mediating extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascades in hippocampal dentate gyrus.Neuroscience. 2006 Dec;143(3):827-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.031. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 17000055
-
Temporal assessment of histone H3 phospho-acetylation and casein kinase 2 activation in dentate gyrus from ischemic rats.Brain Res. 2009 Dec 11;1302:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.030. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19765564
-
Src kinase up-regulates the ERK cascade through inactivation of protein phosphatase 2A following cerebral ischemia.BMC Neurosci. 2009 Jul 14;10:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-74. BMC Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19602257 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol protects CA1 neurons against focal cerebral ischemic reperfusion-induced damage via the ERK-CREB signaling pathway in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016 Jul-Aug;146-147:21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016. PMID: 27143440
-
c-Src protein tyrosine kinase activity is required for muscarinic receptor-mediated DNA synthesis and neurogenesis via ERK1/2 and c-AMP-responsive element-binding protein signaling in neural precursor cells.J Neurosci Res. 2003 May 1;72(3):334-42. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10591. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 12692900
Cited by
-
Ionotropic receptors and ion channels in ischemic neuronal death and dysfunction.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Jan;34(1):39-48. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.95. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 22864302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ras family small GTPase-mediated neuroprotective signaling in stroke.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2011 Jun 1;11(2):114-37. doi: 10.2174/187152411796011349. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21521171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide ameliorates cardiomyocytes hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by extracellular calcium-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:912310. doi: 10.1155/2013/912310. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 24392181 Free PMC article.
-
Dracohodin Perochlorate Stimulates Fibroblast Proliferation via EGFR Activation and Downstream ERK/CREB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathways In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Aug 25;2019:6027186. doi: 10.1155/2019/6027186. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31534465 Free PMC article.
-
Isoquercetin Ameliorates Cerebral Impairment in Focal Ischemia Through Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Primary Culture of Rat Hippocampal Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Region of Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):2126-2142. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9806-5. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26924319
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

