Computational prediction of essential genes in an unculturable endosymbiotic bacterium, Wolbachia of Brugia malayi
- PMID: 19943957
- PMCID: PMC2794283
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-243
Computational prediction of essential genes in an unculturable endosymbiotic bacterium, Wolbachia of Brugia malayi
Abstract
Background: Wolbachia (wBm) is an obligate endosymbiotic bacterium of Brugia malayi, a parasitic filarial nematode of humans and one of the causative agents of lymphatic filariasis. There is a pressing need for new drugs against filarial parasites, such as B. malayi. As wBm is required for B. malayi development and fertility, targeting wBm is a promising approach. However, the lifecycle of neither B. malayi nor wBm can be maintained in vitro. To facilitate selection of potential drug targets we computationally ranked the wBm genome based on confidence that a particular gene is essential for the survival of the bacterium.
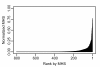
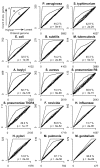
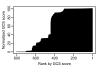
Results: wBm protein sequences were aligned using BLAST to the Database of Essential Genes (DEG) version 5.2, a collection of 5,260 experimentally identified essential genes in 15 bacterial strains. A confidence score, the Multiple Hit Score (MHS), was developed to predict each wBm gene's essentiality based on the top alignments to essential genes in each bacterial strain. This method was validated using a jackknife methodology to test the ability to recover known essential genes in a control genome. A second estimation of essentiality, the Gene Conservation Score (GCS), was calculated on the basis of phyletic conservation of genes across Wolbachia's parent order Rickettsiales. Clusters of orthologous genes were predicted within the 27 currently available complete genomes. Druggability of wBm proteins was predicted by alignment to a database of protein targets of known compounds.
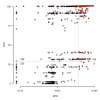
Conclusion: Ranking wBm genes by either MHS or GCS predicts and prioritizes potentially essential genes. Comparison of the MHS to GCS produces quadrants representing four types of predictions: those with high confidence of essentiality by both methods (245 genes), those highly conserved across Rickettsiales (299 genes), those similar to distant essential genes (8 genes), and those with low confidence of essentiality (253 genes). These data facilitate selection of wBm genes for entry into drug design pipelines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Wolbachia genome of Brugia malayi: endosymbiont evolution within a human pathogenic nematode.PLoS Biol. 2005 Apr;3(4):e121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030121. Epub 2005 Mar 29. PLoS Biol. 2005. PMID: 15780005 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of transcription factors that regulate the type IV secretion system and riboflavin biosynthesis in Wolbachia of Brugia malayi.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051597. Epub 2012 Dec 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251587 Free PMC article.
-
The heme biosynthetic pathway of the obligate Wolbachia endosymbiont of Brugia malayi as a potential anti-filarial drug target.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009 Jul 14;3(7):e475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000475. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 19597542 Free PMC article.
-
Wolbachia genomes: revealing the biology of parasitism and mutualism.Trends Parasitol. 2006 Feb;22(2):60-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2005.12.012. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Trends Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16406333 Review.
-
Wolbachia genomes: insights into an intracellular lifestyle.Curr Biol. 2005 Jul 12;15(13):R507-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.029. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16005284 Review.
Cited by
-
The genome of the heartworm, Dirofilaria immitis, reveals drug and vaccine targets.FASEB J. 2012 Nov;26(11):4650-61. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-205096. Epub 2012 Aug 13. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22889830 Free PMC article.
-
Training set selection for the prediction of essential genes.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 22;9(1):e86805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086805. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24466248 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Computational Approach for Identifying Essential Proteins From Multiplex Biological Networks.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 21;11:343. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00343. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32373163 Free PMC article.
-
Putative essential and core-essential genes in Mycoplasma genomes.Sci Rep. 2011;1:53. doi: 10.1038/srep00053. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Sci Rep. 2011. PMID: 22355572 Free PMC article.
-
A new computational strategy for predicting essential genes.BMC Genomics. 2013 Dec 21;14:910. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-910. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24359534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agüero F, Al-Lazikani B, Aslett M, Berriman M, Buckner FS, Campbell RK, Carmona S, Carruthers IM, Chan AW, Chen F, Crowther GJ, Doyle MA, Hertz-Fowler C, Hopkins AL, McAllister G, Nwaka S, Overington JP, Pain A, Paolini GV, Pieper U, Ralph SA, Riechers A, Roos DS, Sali A, Shanmugam D, Suzuki T, van Voorhis WC, Verlinde CL. Genomic-scale prioritization of drug targets: the TDR Targets database. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(11):900–7. doi: 10.1038/nrd2684. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

