Birth time/order-dependent neuron type specification
- PMID: 19944594
- PMCID: PMC2837925
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2009.10.017
Birth time/order-dependent neuron type specification
Abstract
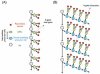
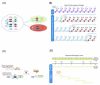
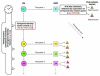
Neurons derived from the same progenitor may acquire different fates according to their birth timing/order. To reveal temporally guided cell fates, we must determine neuron types as well as their lineage relationships and times of birth. Recent advances in genetic lineage analysis and fate mapping are facilitating such studies. For example, high-resolution lineage analysis can identify each sequentially derived neuron of a lineage and has revealed abrupt temporal identity changes in diverse Drosophila neuronal lineages. In addition, fate mapping of mouse neurons made from the same pool of precursors shows production of specific neuron types in specific temporal patterns. The tools used in these analyses are helping to further our understanding of the genetics of neuronal temporal identity.
2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A complete developmental sequence of a Drosophila neuronal lineage as revealed by twin-spot MARCM.PLoS Biol. 2010 Aug 24;8(8):e1000461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000461. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20808769 Free PMC article.
-
A novel temporal identity window generates alternating Eve+/Nkx6+ motor neuron subtypes in a single progenitor lineage.Neural Dev. 2020 Jul 28;15(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13064-020-00146-6. Neural Dev. 2020. PMID: 32723364 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage analysis of Drosophila lateral antennal lobe neurons reveals notch-dependent binary temporal fate decisions.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(11):e1001425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001425. Epub 2012 Nov 20. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 23185131 Free PMC article.
-
Specification of neurons through asymmetric cell divisions.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010 Feb;20(1):44-9. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2009.09.014. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 19896361 Review.
-
Generating neuronal diversity in the Drosophila central nervous system.Dev Dyn. 2012 Jan;241(1):57-68. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22739. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Dev Dyn. 2012. PMID: 21932323 Review.
Cited by
-
Convergent microRNA actions coordinate neocortical development.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Aug;71(16):2975-95. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1576-5. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24519472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deterministic and probabilistic fate decisions co-exist in a single retinal lineage.EMBO J. 2023 Jul 17;42(14):e112657. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112657. Epub 2023 May 15. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37184124 Free PMC article.
-
The Hunchback temporal transcription factor determines motor neuron axon and dendrite targeting in Drosophila.Development. 2019 Apr 5;146(7):dev175570. doi: 10.1242/dev.175570. Development. 2019. PMID: 30890568 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cycle-independent transitions in temporal identity of mammalian neural progenitor cells.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 20;7:11349. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11349. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27094546 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical deployment of factors regulating temporal fate in a diverse neuronal lineage of the Drosophila central brain.Neuron. 2012 Feb 23;73(4):677-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.018. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22365543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jessell TM. Neuronal specification in the spinal cord: inductive signals and transcriptional codes. Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Urbach R, Technau GM. Early steps in building the insect brain: neuroblast formation and segmental patterning in the developing brain of different insect species. Arthropod Structure&Development. 2003;32:103–123. - PubMed
-
- Skeath J, Thor S. Genetic control of Drosophila nerve cord development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Technau GM, Berger C, Urbach R. Generation of cell diversity and segmental pattern in the embryonic central nervous system of Drosophila. Dev Dyn. 2006;235:861–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

