Neuroimmune mechanisms of cytokine-induced depression: current theories and novel treatment strategies
- PMID: 19944762
- PMCID: PMC2995293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.11.015
Neuroimmune mechanisms of cytokine-induced depression: current theories and novel treatment strategies
Abstract
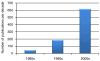
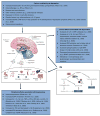
The relationships between immune and neural function are an increasingly important area of study for neuropsychiatric disorders, in particular depression. This is exemplified by the growing number of publications on cytokines and depression during the last 10 years, as compared to earlier decades. This review summarizes the current theories and novel treatment strategies for depression, with a focus on cytokine-induced depression. Neuroimmune mechanisms are now viewed as central to the development of depressive symptoms and emerging evidence is beginning to identify the neural circuits involved in cytokine-induced depression. The current diagnostic categories for depression, as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, however, are not etiologically or biologically derived, and it has been proposed that "depression", likely reflects multiple pathogeneses leading to varying symptom constellations. As we move toward a better biological understanding of depression-related symptom constellations or syndromes, the term "depression" may prove inadequately broad, and an integration of interdisciplinary literatures will increase in importance. Future research should aim to characterize these depression-related symptom constellations or syndromes better with the goal of optimizing treatment strategies.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilera M, Arias B, Wichers M, Barrantes-Vidal N, Moya J, Villa H, van Os J, Ibáñez MI, Ruipérez MA, Ortet G, Fañanás L. Early adversity and 5-HTT/BDNF genes: new evidence of gene–environment interactions on depressive symptoms in a general population. Psychol Med. 2009;39:1425–1432. - PubMed
-
- Akhondzadeh S, Jafari S, Raisi F, Nasehi AA, Ghoreishi A, Salehi B, Mohebbi-Rasa S, Raznahan M, Kamalipour A. Clinical trial of adjunctive celecoxib treatment in patients with major depression: a double blind and placebo controlled trial. Depress Anxiety. 2009;26(7):607–611. - PubMed
-
- Anisman H, Kokkinidis L, Borowski T, Merali Z. Differential effects of interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-2 and IL-6 on responding for rewarding lateral hypothalamic stimulation. Brain Res. 1998;779:177–187. - PubMed
-
- Anisman H, Poulter MO, Gandhi R, Merali Z, Hayley S. Interferon-alpha effects are exaggerated when administered on a psychosocial stressor backdrop: cytokine, corticosterone and brain monoamine variations. J Neuroimmunol. 2007a;186:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Anisman H, Prakash P, Merali Z, Poulter MO. Corticotropin releasing hormone receptor alterations elicited by acute and chronic unpredictable stressor challenges in stressor-susceptible and resilient strains of mice. Behav Brain Res. 2007b;181:180–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

