Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the term infant
- PMID: 19944838
- PMCID: PMC2849741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2009.07.011
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the term infant
Abstract
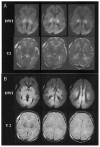
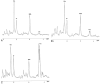
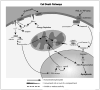
Hypoxia-ischemia in the perinatal period is an important cause of cerebral palsy and associated disabilities in children. There has been significant research progress in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy over the last 2 decades, and many new molecular mechanisms have been identified. Despite all these advances, therapeutic interventions are still limited. In this article the authors discuss several molecular pathways involved in hypoxia-ischemia, and potential therapeutic targets.
Figures

References
-
- Johnston MV, Hoon AH., Jr Cerebral palsy. Neuromolecular Med. 2006;8(4):435–450. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli A, Incerti M, Ghidini A, Greco M, Villa E, Paterlini G. Factors associated with umbilical artery acidemia in term infants with low Apgar scores at 5 min. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008 Aug;139(2):146–150. - PubMed
-
- Graham EM, Ruis KA, Hartman AL, Northington FJ, Fox HE. A systematic review of the role of intrapartum hypoxia-ischemia in the causation of neonatal encephalopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Dec;199(6):587–595. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Li J, Gu M. The correlation between myocardial function and cerebral hemodynamics in term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Trop Pediatr. 2007 Feb;53(1):44–48. - PubMed
-
- Volpe JJ. Perinatal brain injury: from pathogenesis to neuroprotection. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2001;7(1):56–64. - PubMed

