Lipid and glycolipid antigens of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells
- PMID: 19945296
- PMCID: PMC2837800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2009.10.003
Lipid and glycolipid antigens of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells
Abstract
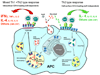
In spite of their relatively limited antigen receptor repertoire, CD1d-restricted NKT cells recognize a surprisingly diverse range of lipid and glycolipid antigens. Recent studies of natural and synthetic CD1d-presented antigens provide an increasingly detailed picture of how the specific structural features of these lipids and glycolipids influence their ability to be presented to NKT cells and stimulate their diverse immunologic functions. Particularly for synthetic analogues of alpha-galactosylceramides which have been the focus of intense recent investigation, it is becoming clear that the design of glycolipid antigens with the ability to precisely control the specific immunologic activities of NKT cells is likely to be feasible. The emerging details of the mechanisms underlying the structure-activity relationship of NKT cell antigens will assist greatly in the design and production of immunomodulatory agents for the precise manipulation of NKT cells and the many other components of the immune system that they influence.
Figures
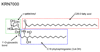
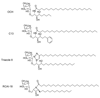
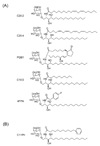
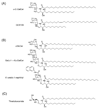
References
-
- Behar SM, Porcelli SA. CD1-restricted T cells in host defense to infectious diseases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;314:215–250. - PubMed
-
- Wu L, Van Kaer L. Natural killer T cells and autoimmune disease. Curr Mol Med. 2009;9:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey DI, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M, Smyth MJ, Van Kaer L. NKT cells: what's in a name? Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:231–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

