DSCAM and DSCAML1 function in self-avoidance in multiple cell types in the developing mouse retina
- PMID: 19945391
- PMCID: PMC2850049
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.027
DSCAM and DSCAML1 function in self-avoidance in multiple cell types in the developing mouse retina
Abstract
DSCAM and DSCAM-LIKE1 (DSCAML1) serve diverse neurodevelopmental functions, including axon guidance, synaptic adhesion, and self-avoidance, depending on the species, cell type, and gene family member studied. We examined the function of DSCAM and DSCAML1 in the developing mouse retina. In addition to a subset of amacrine cells, Dscam was expressed in most retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). RGCs had fasciculated dendrites and clumped cell bodies in Dscam(-/-) mice, suggesting a role in self-avoidance. Dscaml1 was expressed in the rod circuit, and mice lacking Dscaml1 had fasciculated rod bipolar cell dendrites and clumped AII amacrine cell bodies, also indicating a role in self-avoidance. Neurons in Dscam or Dscaml1 mutant retinas stratified their processes appropriately in synaptic laminae in the inner plexiform layer, and functional synapses formed in the rod circuit in mice lacking Dscaml1. Therefore, DSCAM and DSCAML1 function similarly in self-avoidance, and are not essential for synaptic specificity in the mouse retina.
Figures
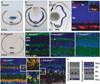
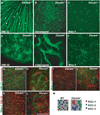
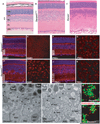
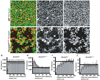
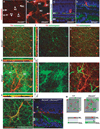
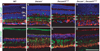
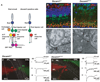
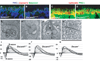
Comment in
-
Mammalian DSCAMs: they won't help you find a partner, but they'll guarantee you some personal space.Neuron. 2009 Nov 25;64(4):441-3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.011. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19945385 Review.
References
-
- Agarwala KL, Ganesh S, Tsutsumi Y, Suzuki T, Amano K, Yamakawa K. Cloning and functional characterization of DSCAML1, a novel DSCAM-like cell adhesion molecule that mediates homophilic intercellular adhesion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285:760–772. - PubMed
-
- Chen BE, Kondo M, Garnier A, Watson FL, Puettmann-Holgado R, Lamar DR, Schmucker D. The molecular diversity of Dscam is functionally required for neuronal wiring specificity in Drosophila. Cell. 2006;125:607–620. - PubMed
-
- Coombs J, van der List D, Wang GY, Chalupa LM. Morphological properties of mouse retinal ganglion cells. Neuroscience. 2006;140:123–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

