Prevention of steatosis by hepatic JNK1
- PMID: 19945406
- PMCID: PMC2804105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.09.007
Prevention of steatosis by hepatic JNK1
Abstract
Nonalcoholic steatosis (fatty liver) is a major cause of liver dysfunction that is associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. The cJun NH(2)-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) signaling pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis and drugs that target JNK1 may be useful for treatment of this disease. Indeed, mice with defects in JNK1 expression in adipose tissue are protected against hepatic steatosis. Here we report that mice with specific ablation of Jnk1 in hepatocytes exhibit glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. JNK1 therefore serves opposing actions in liver and adipose tissue to both promote and prevent hepatic steatosis. This finding has potential implications for the design of JNK1-selective drugs for the treatment of metabolic syndrome.
Figures
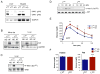
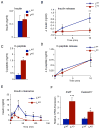
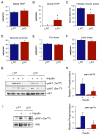
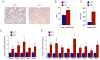
Comment in
-
c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 1 in hepatocytes: an essential mediator of insulin resistance.Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2221-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.23737. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20513007 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis RJ, White MF. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307) J Biol Chem. 2000;275:9047–9054. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P, Lindor KD. Treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;16:797–810. - PubMed
-
- Bonny C, Oberson A, Negri S, Sauser C, Schorderet DF. Cell-permeable peptide inhibitors of JNK: novel blockers of beta-cell death. Diabetes. 2001;50:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Selective versus total insulin resistance: a pathogenic paradox. Cell Metab. 2008;7:95–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

