Functional near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) signal improvement based on negative correlation between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin dynamics
- PMID: 19945536
- PMCID: PMC2818571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.050
Functional near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) signal improvement based on negative correlation between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin dynamics
Abstract
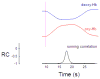
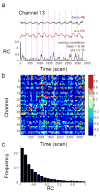
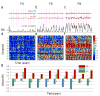
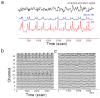
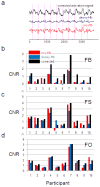
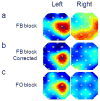
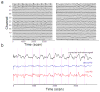
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a promising technology for functional brain imaging which measures hemodynamic signals from the cortex, similar to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), but does not require the participant to lie motionless in a confined space. NIRS can therefore be used for more naturalistic experiments, including face to face communication, or natural body movements, and is well suited for real-time applications that may require lengthy training. However, improving signal quality and reducing noise, especially noise induced by head motion, is challenging, particularly for real time applications. Here we study the properties of head motion induced noise, and find that motion noise causes the measured oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin signals, which are typically strongly negatively correlated, to become more positively correlated. Next, we develop a method to reduce noise based on the principle that the concentration changes of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin should be negatively correlated. We show that despite its simplicity, this method is effective in reducing noise and improving signal quality, for both online and offline noise reduction.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bauernfeind G, Leeb R, Wriessnegger SC, Pfurtscheller G. Development, set-up and first results for a one-channel near-infrared spectroscopy system. Biomedizinische Technik. Biomedical engineering. 2008;53:36–43. - PubMed
-
- Boas DA, Strangman G, Culver JP, Hoge RD, Jasdzewski G, Poldrack RA, Rosen BR, Mandeville JB. Can the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen be estimated with near-infrared spectroscopy? Physics in medicine and biology. 2003;48:2405–18. - PubMed
-
- Buxton RB, Uludag K, Dubowitz DJ, Liu TT. Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation. Neuroimage. 2004;23(Suppl 1):S220–33. - PubMed
-
- Buxton RB, Wong EC, Frank LR. Dynamics of blood flow and oxygenation changes during brain activation: the balloon model. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 1998;39:855–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

