X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor
- PMID: 19946266
- PMCID: PMC2861655
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08624
X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor
Abstract
Ionotropic glutamate receptors mediate most excitatory neurotransmission in the central nervous system and function by opening a transmembrane ion channel upon binding of glutamate. Despite their crucial role in neurobiology, the architecture and atomic structure of an intact ionotropic glutamate receptor are unknown. Here we report the crystal structure of the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA)-sensitive, homotetrameric, rat GluA2 receptor at 3.6 A resolution in complex with a competitive antagonist. The receptor harbours an overall axis of two-fold symmetry with the extracellular domains organized as pairs of local dimers and with the ion channel domain exhibiting four-fold symmetry. A symmetry mismatch between the extracellular and ion channel domains is mediated by two pairs of conformationally distinct subunits, A/C and B/D. Therefore, the stereochemical manner in which the A/C subunits are coupled to the ion channel gate is different from the B/D subunits. Guided by the GluA2 structure and site-directed cysteine mutagenesis, we suggest that GluN1 and GluN2A NMDA (N-methyl-d-aspartate) receptors have a similar architecture, with subunits arranged in a 1-2-1-2 pattern. We exploit the GluA2 structure to develop mechanisms of ion channel activation, desensitization and inhibition by non-competitive antagonists and pore blockers.
Figures
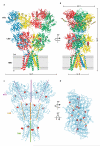
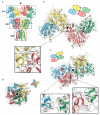
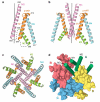
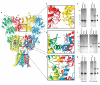
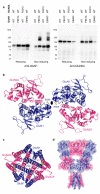

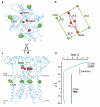
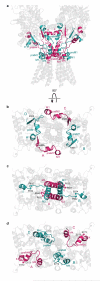
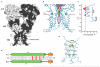
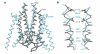
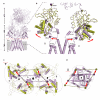
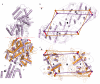
Comment in
-
Neuroscience: Excitatory view of a receptor.Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):729-31. doi: 10.1038/462729a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 20010675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cowan WM, Sudhof TC, Stevens CF, editors. Synapses. The Johns Hopkins University Press; Baltimore, MD: 2001.
-
- Hayashi T. Effects of sodium glutamate on the nervous system. Keio J. Med. 1954;3:183–192.
-
- Curtis DR, Phillis JW, Watkins JC. Chemical excitation of spinal neurons. Nature. 1959;183:611. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama H, Ito I, Watanabe M. Glutamate receptor subtypes may be classified into two major categories: A study on Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. Neuron. 1989;3:129–132. - PubMed
-
- Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacological Rev. 1999;51:7–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

